Difference between revisions of "At-Large Advisory Committee"
Dana Silvia (talk | contribs) (Short overview, ALAC History, At-Large Structures, ALAC Responsibilities) |
|||
| (63 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | The '''At-Large Advisory Committee (ALAC)''' is one of [[ICANN]]'s [[AC|Advisory Committees]]. The mission of ALAC is to function as an advocate for the interests of individual Internet users. | |
| − | == | + | ==Overview== |
| − | [[ | + | The 15-member ALAC represents the [[At-Large Community]] and consists of two members selected by each of the five [[RALO]]s and five members appointed by ICANN's [[NomCom| Nominating Committee]]. The committee is tasked with advocating for the interests of end-users, advising on the Internet policies developed by ICANN's [[Supporting Organizations]], and selecting a director to serve on the [[ICANN Board]]. ALAC also plays a significant role in ICANN's outreach and engagement programs. |
| − | == | + | ===History=== |
| − | + | For a timeline of ALAC's activity over the course of ICANN, see [[ALAC Timeline]]. Key events include: | |
| − | + | The [[ICANN Board]] adopted new bylaws on October 31, 2002, which came into effect on December 15, 2002. The creation of the ALAC was part of a larger reform effort within ICANN, now known as ICANN 2.0. The new bylaws established the ALAC and provided support for At-Large Organizations. It stated that the ALAC should consist of ten members selected by [[RALO|Regional At-Large Organizations]], with five supplementary members to be selected by [[NomCom|ICANN's Nominating Committee]]. The interim ALAC consisted of ten members, two from each of ICANN's 5 regions.<ref>[http://www.icann.org/en/committees/alac/ ALAC History]</ref> | |
| − | |||
| − | == | + | In her testimony to the Senate Committee on Commerce, Science & Transportation on December 8, 2011, [[Esther Dyson]], former Chair of the ICANN Board and ALAC member, noted the difficulty of representing the average Internet user within ICANN, even with the ALAC. Specific problems included recruiting members and fostering productive message boards and long-distance communications.<ref>[http://commerce.senate.gov/public/?a=Files.Serve&File_id=c81ce454-f519-4373-a51d-234c61755e39 Commerce.Senate.gov]</ref> Since then, ALAC has focused its attention on addressing these issues, among others, to cultivate more and better participation by end-users in the At-Large Community.<ref>[https://atlarge.icann.org/get-involved At-Large Get Involved]</ref> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==The Role of the ALAC== | |
| + | In accordance with [[ICANN Bylaws]], the ALAC is charged with understanding, representing, and advocating for the best interest of Internet end users worldwide. The ALAC focuses on two general areas of work: policy advice development and organization building.<ref>[https://atlarge.icann.org/about/what-does-alac-do What Does ALAC Do?]</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Policy Advice Development=== | ||
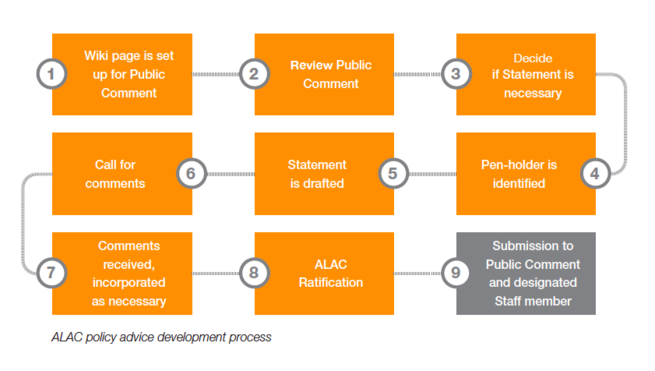
| + | [[File:ALAC Policy Advice Development Process.png|655px|thumbnail|right|ALAC Policy Advice Development (Image from ICANN.org)]]The ALAC does not develop policy; it publicizes, analyzes, and provides advice on ICANN policy proposals and decisions. [[Public Comment]] proceedings are the main channel through which the ALAC advises ICANN. It also corresponds with and responds to input requests from other ICANN body working groups. | ||
| + | |||
| + | When a new [[Public Comment]] opens, the ALAC consults with subject matter experts within the [[At-Large Community]] to decide if it should make a statement on the topic. It uses mailing lists, RALO, and working groups to build consensus. Then, the ALAC determines who should be the “penholders,” the individuals responsible for the initial draft of the statement to be submitted to the Public Comment. The completed draft is posted on the ALAC Wiki workspace for comment and then it is finalized. Then the 15 ALAC members ratify and submit the document to the Public Comment as a formal ALAC Policy Advice Statement. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Organization Building=== | ||
| + | The ALAC seeks to ensure sure that all [[ALS]]es and individual members understand [[ICANN |ICANN’s mission and core value]], contribute to policy developments, and sustain the flow of end-user volunteers into the [[Multistakeholder Model]] of ICANN. The committee does in three ways: capacity building, outreach, and operational matters, all of which focus on cultivating RALOs and ALSes. The most formalized of the ALAC’s means is its operational contributions, which include: | ||
| + | #[[ALS]] accreditation | ||
| + | #Meeting planning for ALAC, RALOs, and At-Large working group sessions during ICANN International Meetings. | ||
| + | #Budget request review from RALOs for outreach, engagement, or capacity building | ||
| + | #Selection of members – Evaluate and confirm candidates selected from the [[At-Large Community]] as delegates to the [[NomCom]] and [[Cross Community Working Groups]] | ||
| + | #Organizational review | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==At-Large Structures== | ||
| + | :''Main article: [[ALS]]'' | ||
| + | The ALAC represents a network of regionally self-organized and self-supporting At-Large Structures, which represent individual Internet users throughout the world. | ||
| + | The At-Large Structures are divided into five Regional At-Large Organizations (one in each [[ICANN]] region – Africa, Asia-Pacific, Europe, Latin America/Caribbean, and North America). These RALOs manage public involvement and represent their constituents to ICANN.<ref>[http://www.icann.org/en/committees/alac/ ICANN At-Large structures]</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Through these At-Large Structures, individual internet users have been given a voice and a space whereby they can influence the policy decisions made by ICANN.<ref>[http://icannwiki.org/ALAC About ALAC]</ref> | ||
==ALAC responsibilities== | ==ALAC responsibilities== | ||
| − | Besides following the provisions of ICANN | + | Besides following the provisions of ICANN's new bylaws, ALAC has responsibilities such as assisting the formation and qualification of other At-Large Structures and [[RALO]]s. |
| − | Other responsibilities undertaken by ALAC and its organizations | + | Other responsibilities undertaken by ALAC and its organizations include: |
| − | * Evaluating | + | * Evaluating the accreditation process for At-Large Structures |
| − | * Analyzing and publishing ICANN's policies and decisions | + | * Analyzing and publishing ICANN's policies and decisions |
| − | * Providing guidance and advice to various organizations regarding ICANN's proposals and activities which are relevant for Internet | + | * Coordinating with the [[GNSO]] and other ICANN committees |
| + | * Providing guidance and advice to various organizations regarding ICANN's proposals and activities which are relevant for individual Internet users | ||
* Analyzing and approving the applications of At-Large Structures | * Analyzing and approving the applications of At-Large Structures | ||
| − | * Developing Internet-based processes and methods to enable and ease the communication process between At-Large structures <ref>[http://www.icann.org/en/committees/alac/ ALAC responsibilities]</ref> | + | * Developing Internet-based processes and methods to enable and ease the communication process between At-Large structures<ref>[http://www.icann.org/en/committees/alac/ ALAC responsibilities]</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | ==ALAC Leadership== | ||
| + | '''Africa''' | ||
| + | * [[Dave Kissoondoyal]], '''Leadership Team Member''', Mauritius 2019 AGM - 2023 AGM | ||
| + | * [[Sarah Kiden]], Uganda, 2020 AGM - 2024 AGM | ||
| + | * [[Raymond Selorm Mamattah]], Ghana, [[Nominating Committee Appointees]], 2021 AGM - 2023 AGM | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Asia/Australia and the Pacific Islands''' | ||
| + | * [[Rao Naveed Bin Rais]] United Arab Emirates, 2021 AGM - 2023 AGM | ||
| + | * [[Maureen Hilyard]], '''Vice Chair''', Cook Islands, 2019 AGM - 2023 AGM | ||
| + | * [[Satish Babu]] India, 2022 AGM - 2024 AGM | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Europe''' | ||
| + | * [[Joanna Kulesza]], '''Vice Chair''', Poland, 2020 AGM - 2024 AGM | ||
| + | * [[Matthias Markus Hudobnik]], Austria, 2019 AGM - 2023 AGM | ||
| + | * [[Tommi Karttaavi]] Finland, [[Nominating Committee Appointees]], 2022 AGM - 2024 AGM | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Latin America and the Caribbean Islands''' | ||
| + | * [[Laura Margolis]], Uruguay, [[Nominating Committee Appointees]], 2021 AGM - 2023 AGM | ||
| + | * [[Marcelo Rodriguez]] Argentina, 2022 AGM - 2024 AGM | ||
| + | * [[Carlos Aguirre]], Argentina, 2021 AGM - 2023 AGM | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''North America''' | ||
| + | * [[Bill Jouris]] US, 2022 AGM - 2024 AGM | ||
| + | * [[Jonathan Zuck]], '''Chair''' United States of America, 2019 AGM - 2023 AGM | ||
| + | * [[Eduardo Diaz]] Puerto Rico, [[Nominating Committee Appointees]], 2022 AGM - 2024 AGM | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''ALAC Liaisons''' | ||
| + | *[[Lianna Galstyan]], Armenia, [[ccNSO]] | ||
| + | *[[Justine Chew]], Singapore, [[GNSO]] | ||
| + | *[[Joanna Kulesza]], Poland, [[Governmental Advisory Committee|GAC]] | ||
| + | *[[Andrei Kolesnikov]], Russia, [[SSAC]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist}} | {{Reflist}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category: ICANN Bodies]] |
| + | __FORCETOC__ | ||
Latest revision as of 16:59, 10 January 2023
The At-Large Advisory Committee (ALAC) is one of ICANN's Advisory Committees. The mission of ALAC is to function as an advocate for the interests of individual Internet users.
Overview
The 15-member ALAC represents the At-Large Community and consists of two members selected by each of the five RALOs and five members appointed by ICANN's Nominating Committee. The committee is tasked with advocating for the interests of end-users, advising on the Internet policies developed by ICANN's Supporting Organizations, and selecting a director to serve on the ICANN Board. ALAC also plays a significant role in ICANN's outreach and engagement programs.
History
For a timeline of ALAC's activity over the course of ICANN, see ALAC Timeline. Key events include: The ICANN Board adopted new bylaws on October 31, 2002, which came into effect on December 15, 2002. The creation of the ALAC was part of a larger reform effort within ICANN, now known as ICANN 2.0. The new bylaws established the ALAC and provided support for At-Large Organizations. It stated that the ALAC should consist of ten members selected by Regional At-Large Organizations, with five supplementary members to be selected by ICANN's Nominating Committee. The interim ALAC consisted of ten members, two from each of ICANN's 5 regions.[1]
In her testimony to the Senate Committee on Commerce, Science & Transportation on December 8, 2011, Esther Dyson, former Chair of the ICANN Board and ALAC member, noted the difficulty of representing the average Internet user within ICANN, even with the ALAC. Specific problems included recruiting members and fostering productive message boards and long-distance communications.[2] Since then, ALAC has focused its attention on addressing these issues, among others, to cultivate more and better participation by end-users in the At-Large Community.[3]
The Role of the ALAC
In accordance with ICANN Bylaws, the ALAC is charged with understanding, representing, and advocating for the best interest of Internet end users worldwide. The ALAC focuses on two general areas of work: policy advice development and organization building.[4]
Policy Advice Development
The ALAC does not develop policy; it publicizes, analyzes, and provides advice on ICANN policy proposals and decisions. Public Comment proceedings are the main channel through which the ALAC advises ICANN. It also corresponds with and responds to input requests from other ICANN body working groups.
When a new Public Comment opens, the ALAC consults with subject matter experts within the At-Large Community to decide if it should make a statement on the topic. It uses mailing lists, RALO, and working groups to build consensus. Then, the ALAC determines who should be the “penholders,” the individuals responsible for the initial draft of the statement to be submitted to the Public Comment. The completed draft is posted on the ALAC Wiki workspace for comment and then it is finalized. Then the 15 ALAC members ratify and submit the document to the Public Comment as a formal ALAC Policy Advice Statement.
Organization Building
The ALAC seeks to ensure sure that all ALSes and individual members understand ICANN’s mission and core value, contribute to policy developments, and sustain the flow of end-user volunteers into the Multistakeholder Model of ICANN. The committee does in three ways: capacity building, outreach, and operational matters, all of which focus on cultivating RALOs and ALSes. The most formalized of the ALAC’s means is its operational contributions, which include:
- ALS accreditation
- Meeting planning for ALAC, RALOs, and At-Large working group sessions during ICANN International Meetings.
- Budget request review from RALOs for outreach, engagement, or capacity building
- Selection of members – Evaluate and confirm candidates selected from the At-Large Community as delegates to the NomCom and Cross Community Working Groups
- Organizational review
At-Large Structures
- Main article: ALS
The ALAC represents a network of regionally self-organized and self-supporting At-Large Structures, which represent individual Internet users throughout the world. The At-Large Structures are divided into five Regional At-Large Organizations (one in each ICANN region – Africa, Asia-Pacific, Europe, Latin America/Caribbean, and North America). These RALOs manage public involvement and represent their constituents to ICANN.[5]
Through these At-Large Structures, individual internet users have been given a voice and a space whereby they can influence the policy decisions made by ICANN.[6]
ALAC responsibilities
Besides following the provisions of ICANN's new bylaws, ALAC has responsibilities such as assisting the formation and qualification of other At-Large Structures and RALOs. Other responsibilities undertaken by ALAC and its organizations include:
- Evaluating the accreditation process for At-Large Structures
- Analyzing and publishing ICANN's policies and decisions
- Coordinating with the GNSO and other ICANN committees
- Providing guidance and advice to various organizations regarding ICANN's proposals and activities which are relevant for individual Internet users
- Analyzing and approving the applications of At-Large Structures
- Developing Internet-based processes and methods to enable and ease the communication process between At-Large structures[7]
ALAC Leadership
Africa
- Dave Kissoondoyal, Leadership Team Member, Mauritius 2019 AGM - 2023 AGM
- Sarah Kiden, Uganda, 2020 AGM - 2024 AGM
- Raymond Selorm Mamattah, Ghana, Nominating Committee Appointees, 2021 AGM - 2023 AGM
Asia/Australia and the Pacific Islands
- Rao Naveed Bin Rais United Arab Emirates, 2021 AGM - 2023 AGM
- Maureen Hilyard, Vice Chair, Cook Islands, 2019 AGM - 2023 AGM
- Satish Babu India, 2022 AGM - 2024 AGM
Europe
- Joanna Kulesza, Vice Chair, Poland, 2020 AGM - 2024 AGM
- Matthias Markus Hudobnik, Austria, 2019 AGM - 2023 AGM
- Tommi Karttaavi Finland, Nominating Committee Appointees, 2022 AGM - 2024 AGM
Latin America and the Caribbean Islands
- Laura Margolis, Uruguay, Nominating Committee Appointees, 2021 AGM - 2023 AGM
- Marcelo Rodriguez Argentina, 2022 AGM - 2024 AGM
- Carlos Aguirre, Argentina, 2021 AGM - 2023 AGM
North America
- Bill Jouris US, 2022 AGM - 2024 AGM
- Jonathan Zuck, Chair United States of America, 2019 AGM - 2023 AGM
- Eduardo Diaz Puerto Rico, Nominating Committee Appointees, 2022 AGM - 2024 AGM
ALAC Liaisons
- Lianna Galstyan, Armenia, ccNSO
- Justine Chew, Singapore, GNSO
- Joanna Kulesza, Poland, GAC
- Andrei Kolesnikov, Russia, SSAC