Difference between revisions of "General Data Protection Regulation"
Dustin Loup (talk | contribs) |
Dustin Loup (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | The '''Global Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)''' or '''Regulation (EU) 2016/679'''<ref>[http://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2016/679/oj Regulation (EU) 2016/679 of the European Parliament and of the Council] 27 April 2016</ref> is a regulation aimed at protecting all EU citizens and residents from privacy and data breaches. It was adopted on 14 April 2016 by the European Parliament (EP) after four years of collaborative drafting and negotiations.<ref>[https://www.lexology.com/library/detail.aspx?g=48ffff43-a5cd-40d3-ac1d-6c0a43cd4d21 Lexology - EU General Data Protection Regulation Finally Adopted] 15 April 2016</ref> The regulation is also an update of Data Protection Directive. | + | The '''Global Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)''' or '''Regulation (EU) 2016/679'''<ref>[http://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2016/679/oj Regulation (EU) 2016/679 of the European Parliament and of the Council] 27 April 2016</ref> is a regulation aimed at protecting all EU citizens and residents from privacy and data breaches. It was adopted on 14 April 2016 by the European Parliament (EP) after four years of collaborative drafting and negotiations.<ref>[https://www.lexology.com/library/detail.aspx?g=48ffff43-a5cd-40d3-ac1d-6c0a43cd4d21 Lexology - EU General Data Protection Regulation Finally Adopted] 15 April 2016</ref> The regulation is also an update of Data Protection Directive. Enforcement for the GDPR goes into effect on 25 May 2018.<ref>[http://ec.europa.eu/justice/data-protection/reform/index_en.htm Reform of EU data protection rules]. Retrieved 27 Jun 2017. |
| + | </ref> | ||
| − | The GDPR places specific legal obligations on ' | + | The GDPR places specific legal obligations on 'controllers' and 'processors', those who acts as intermediaries between the user/consumer and themselves, the government or any other actor. The controller determines how and why data is processed and processors act on the controller's behalf. Processors maintain data records and are held responsible in case of a breach. |
With the update on existing legislation, the GDPR is more precise and inclusive of what constitutes private information than its predecessor. Personal data, that is anything that can identify a user, including an [[IP Address|IP address]] is included, as well as 'sensitive personal data' which may include genetic and biomedical data. | With the update on existing legislation, the GDPR is more precise and inclusive of what constitutes private information than its predecessor. Personal data, that is anything that can identify a user, including an [[IP Address|IP address]] is included, as well as 'sensitive personal data' which may include genetic and biomedical data. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==GDPR and WHOIS== | ==GDPR and WHOIS== | ||
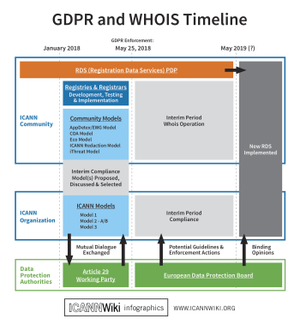
| − | [[File:GDPRTimeline.png| | + | [[File:GDPRTimeline.png|300px|right]] |
| − | + | The GDPR directly impacts the domain name space, most notability the [[WHOIS]] service. Prior to the GDPR enforcement date, [[ICANN]]'s contracted parties ([[Registry|Registries]] and [[Registrar]]s) expressed concern about their about to comply with their contractual requirement and be GDPR compliant. In light of this concern and the uncertainty around the implications of GDPR on WHOIS, ICANN announced that it would defer action against registries and registrars for noncompliance related to registration data.<ref>[https://www.icann.org/resources/pages/contractual-compliance-statement-2017-11-02-en ICANN Contractual Compliance Statement] Accessed 2 February 2018</ref> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 15:29, 2 February 2018
The Global Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or Regulation (EU) 2016/679[1] is a regulation aimed at protecting all EU citizens and residents from privacy and data breaches. It was adopted on 14 April 2016 by the European Parliament (EP) after four years of collaborative drafting and negotiations.[2] The regulation is also an update of Data Protection Directive. Enforcement for the GDPR goes into effect on 25 May 2018.[3]
The GDPR places specific legal obligations on 'controllers' and 'processors', those who acts as intermediaries between the user/consumer and themselves, the government or any other actor. The controller determines how and why data is processed and processors act on the controller's behalf. Processors maintain data records and are held responsible in case of a breach.
With the update on existing legislation, the GDPR is more precise and inclusive of what constitutes private information than its predecessor. Personal data, that is anything that can identify a user, including an IP address is included, as well as 'sensitive personal data' which may include genetic and biomedical data.
GDPR and WHOIS
The GDPR directly impacts the domain name space, most notability the WHOIS service. Prior to the GDPR enforcement date, ICANN's contracted parties (Registries and Registrars) expressed concern about their about to comply with their contractual requirement and be GDPR compliant. In light of this concern and the uncertainty around the implications of GDPR on WHOIS, ICANN announced that it would defer action against registries and registrars for noncompliance related to registration data.[4]
References
- ↑ Regulation (EU) 2016/679 of the European Parliament and of the Council 27 April 2016
- ↑ Lexology - EU General Data Protection Regulation Finally Adopted 15 April 2016
- ↑ Reform of EU data protection rules. Retrieved 27 Jun 2017.
- ↑ ICANN Contractual Compliance Statement Accessed 2 February 2018