ICANN 101
Welcome to the world of ICANN!
If you are new, or even if you aren't, here are a list of important terms that you may need to know.
ICANN
ICANN stands for the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers. It is a private, non-profit organization for the management of the Internet DNS, IP Addresses and Autonomous System Numbers, and the structures that underlie them. It runs on an international, multi-stakeholder model.
|
MAIN ARTICLE: SEE ALSO: |
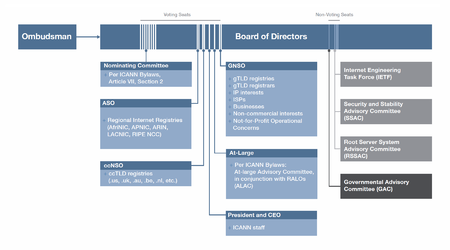
ICANN Organizational Chart |
ASO
- Main article: ASO
- The Address Supporting Organization (ASO) is an ICANN body that develops policies, forms consensus, and makes recommendations to the ICANN Board related to Internet Protocol and addresses.
GAC
- Main article: GAC
- The Government Advisory Committee (GAC) is an ICANN body that consists of representatives from various governments and advises the ICANN Board on public policy issues, national laws, and international agreements.
ALAC
- Main article: ALAC
- The At-Large Advisory Committee (ALAC) is an ICANN body that presents the voices and concerns of individual Internet users, as represented by the At-Large Community.
RSSAC
- Main article: RSSAC
- The Root Server System Advisory Committee (RSSAC) is an ICANN body that advises the ICANN community and Board on issues pertaining to the operation, administration, security, and integrity of the Internet's Root Server System.
SSAC
- Main article: SSAC
- The Security and Stability Advisory Committee (SSAC) is an ICANN body that advises the ICANN Board on matters related to the security and integrity of domain names and the allocation of IP addresses, including security assurance for operational matters, administrative matters, and registrations matters.
NomCom
- Main article: Nominating Committee
- The Nominating Committee (NomCom) is the ICANN body that oversees the selection of various ICANN officers. It is designed to operate independently of all other ICANN bodies and to act in the interest of the global Internet community.
Ombudsman
- Main article: Ombudsman
- The 'Ombudsman is an informal dispute resolution office for members of the ICANN community who wish to lodge complaints about ICANN staff, board, or supporting organizations.
IETF
- Main article: IETF
- The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) is a large open international community of network designers, operators, vendors, and researchers concerned with the evolution of the Internet architecture and the smooth operation of the Internet.
Registry
- Main article: Registry
A registry is the database of all domain names registered under a certain TLD. A registry operator, also called a NIC or network information center, is responsible for managing this database. They contract with registrars, who are accredited to sell domains under the TLD.
Registrar
- Main article: Registrar
A registrar is a company that is authorized to sell domain names.
Registrant
A registrant is a person who has registered a domain name through a registrar.
DNS
The Domain Name System (DNS) translates between alphanumeric domain names and IP Addresses.
TLD
- Main article: TLD
A Top Level Domain (TLD) is the last part of a domain name; for example, .com, .net, .org. The two most prominent types of TLDs are gTLDs and ccTLDs.
gTLD
- Main article: gTLD
A Generic Top-Level Domain (gTLD) refers to any TLD that is not a ccTLD. Previously, gTLDs were limited to being three or more characters. But with the addition of the New TLD program, two character gTLDs may now be registered. Examples of gTLDs include .com, .org, and .info. sTLDs, such as .travel, and GeoTLDs, such as .asia and .cat, are a subset of gTLDs.
New gTLD Program
- Main article: new gTLD Program
- See also: New gTLD Resources
The new gTLD Program is a process by which ICANN accepts applications to add new TLDs to the Root Zone.
ccTLD
- Main article: ccTLD
A Country-Code Top Level Domain (ccTLD) is a TLD with two characters, specifically designed for a particular country, sovereign state or autonomous territory. .uk, .de, and .cn are all examples of ccTLDs.
IP
- Main article: Internet Protocol
- See also: IPv4, IPv6, Internet Protocol Suite
Internet Protocol (IP) is the means by which data is sent from one computer to another via an Internet connection.
IDNs
- Main article: IDNs
Internationalized Domain Names (IDNs) are formed using characters from different scripts, such as Arabic, Chinese, Cyrillic, or Devanagari. These are encoded by the Unicode standard and used as allowed by relevant IDN protocols.