National Institute of Standards and Technology: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
==SP 800 Series== | ==SP 800 Series== | ||
NIST’s Special Publication (SP) 800 series shares computer security information. Created in 1990, the series reports on the Information Technology Laboratory’s research, guidelines, and collaborations with industry, government, and academic organizations.<ref>[https://www.nist.gov/itl/publications-0/nist-special-publication-800-series-general-information SP 800, NIST]</ref> | NIST’s Special Publication (SP) 800 series shares computer security information. Created in 1990, the series reports on the Information Technology Laboratory’s research, guidelines, and collaborations with industry, government, and academic organizations.<ref>[https://www.nist.gov/itl/publications-0/nist-special-publication-800-series-general-information SP 800, NIST]</ref> | ||
==SP 800-37== | |||
The “Guide for Applying the Risk Management Framework to Federal Information Systems” promotes near real-time risk management, encourages the use of automation, integrates information security, emphasizes the selection, implementation, assessment, and overall monitoring of information security controls, links risk management at the information systems level to risks at the organizational level, and establishes responsibility and accountability for security controls.<ref>[https://flank.org/faqs/what-is-nist-sp-800-37 About SP 800-37, Flank]</ref> | |||
NIST SP 800-37 Rev. 2 (RMF 2.0) aka "Risk Management Framework for Information Systems and Organizations: A System Life Cycle Approach for Security and Privacy" superseded RMF 1.0 (above) on December 20, 2019, providing guidelines for applying the RMF to information systems and organizations.<ref>[https://csrc.nist.gov/publications/detail/sp/800-37/rev-1/archive/2014-06-05 ITL Bulletin, NIST]</ref> | |||
==Cybersecurity Framework== | ==Cybersecurity Framework== | ||
Revision as of 16:39, 20 July 2021
| Industry: | Government |
| Founded: | 1901 |
| Headquarters: | Gaithersburg, Maryland |
| Country: | USA |
| Employees: | Approximately 3,400 (2021) |
| Website: | https://www.nist.gov/ |
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is a physical sciences laboratory and non-regulatory agency. As part of the United States Department of Commerce, its mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's laboratory programs include nanotechnology, engineering, information technology, neutron research, material measurement, and physical measurement. The institute was founded on March 3, 1901, as the National Bureau of Standards, and it became NIST in 1988.[1]
Computer Security Resource Center[edit | edit source]
The Computer Security Resource Center (CSRC) has two subdivisions, the CSD and the ACD.[2]
Computer Security Division[edit | edit source]
The CSD is focused on information systems and specializes in Cryptographic Technology; Secure Systems and Applications; Security Components and Mechanisms; Security Engineering and Risk Management; and Security Testing, Validation, and Measurement.
Applied Cybersecurity Division[edit | edit source]
The ACD specializes in Cybersecurity and Privacy Applications, hosts the National Cybersecurity Center of Excellence (NCCoE), and runs the National Initiative for Cybersecurity Education (NICE).
SP 800 Series[edit | edit source]
NIST’s Special Publication (SP) 800 series shares computer security information. Created in 1990, the series reports on the Information Technology Laboratory’s research, guidelines, and collaborations with industry, government, and academic organizations.[3]
SP 800-37[edit | edit source]
The “Guide for Applying the Risk Management Framework to Federal Information Systems” promotes near real-time risk management, encourages the use of automation, integrates information security, emphasizes the selection, implementation, assessment, and overall monitoring of information security controls, links risk management at the information systems level to risks at the organizational level, and establishes responsibility and accountability for security controls.[4]
NIST SP 800-37 Rev. 2 (RMF 2.0) aka "Risk Management Framework for Information Systems and Organizations: A System Life Cycle Approach for Security and Privacy" superseded RMF 1.0 (above) on December 20, 2019, providing guidelines for applying the RMF to information systems and organizations.[5]
Cybersecurity Framework[edit | edit source]
Version 1.0[edit | edit source]
History[edit | edit source]
In February 2013, recognizing the national and economic security of the United States depends on the reliable function of critical infrastructure, President Barak Obama issued Executive Order 13636, "Improving Critical Infrastructure Cybersecurity," ordering NIST to work with stakeholders to develop a voluntary framework based on existing standards, guidelines, and practices for reducing cyber-risks to Critical Infrastructure. On December 18, 2014, the Cybersecurity Enhancement Act of 2014 (CEA) authorized the Department of Commerce, through NIST, to develop voluntary standards to reduce cyber-risks to critical infrastructure.[6] The law also ordered the Office of Science and Technology Policy to develop a federal cybersecurity research and development plan. Section 502 required the Director of NIST to ensure interagency coordination toward the development of international technical standards for IT security and transmit to Congress a plan.
Framework Development[edit | edit source]
February 26, 2013: RFI to Develop a Framework to Improve Critical Infrastructure Cybersecurity - February 12, 2014: Framework 1.0 Publication.
- One year after the release of Executive Order 13636 and following one RFI, five workshops, and one RFC, NIST released version 1.0 of the Framework for Improving Critical Infrastructure Cybersecurity.[7]
Components[edit | edit source]
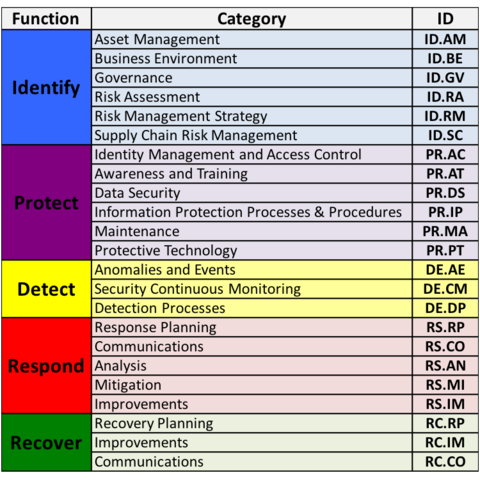
The resulting Cybersecurity Framework consists of voluntary standards, guidelines, and practices for promoting critical infrastructure protection. The Cybersecurity Framework consists of three main components: the Core, Implementation Tiers, and Profiles.[8]
Core[edit | edit source]
The core is a set of desired cybersecurity activities and outcomes organized into Categories and aligned to Informative References.
Tiers[edit | edit source]
The tiers do not describe maturity levels; rather, they describe the degree to which an organization’s cybersecurity risk management practices exhibit the characteristics defined in the Framework. It is up to each organization to decide its target tier. The Tiers range from "partial" to "adaptive," reflecting an increasing degree of rigor, integration among cybersecurity risk decisions, and information sharing between the organization and external parties.[9]
Profiles[edit | edit source]
Profiles refer to the alignment between each organization's requirements and objectives, risk appetite, and resources and the desired outcomes of the Framework. The profile system is meant to help organizations identify opportunities for improving their cybersecurity posture by comparing their current profiles with their target profiles.
C3[edit | edit source]
The Department of Homeland Security's Critical Infrastructure Cyber Community (C3) Voluntary Program helps owners and operators align their organizations with the framework and manage their cyber risks.

