Data Escrow: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Data Escrow''' is the act of storing data with a neutral third party<ref>[http://www.guard-it.com/faqs.html Guard-It.com FAQs]</ref> in case of registry or registrar failure, accreditation termination, or accreditation relapse without renewal. [[ICANN]] requires all registrars and gTLD registries to contract with a data escrow provider in order to safeguard registrants.<ref>[http://www.icann.org/en/news/announcements/announcement-2-09nov07-en.htm Implementation of Registrar Data Escrow Program, icann.org]</ref><ref>[http://archive.icann.org/en/tlds/data-escrow-report05mar07.htm ICANN's gTLD Registry Data Escrow Requirements, icann.org]</ref> | '''Data Escrow''' is the act of storing data with a neutral third party<ref>[http://www.guard-it.com/faqs.html Guard-It.com FAQs] or [https://www.escrowtech.com EscrowTech International, Inc.]</ref> in case of registry or registrar failure, accreditation termination, or accreditation relapse without renewal. [[ICANN]] requires all registrars and gTLD registries to contract with a data escrow provider in order to safeguard registrants.<ref>[http://www.icann.org/en/news/announcements/announcement-2-09nov07-en.htm Implementation of Registrar Data Escrow Program, icann.org]</ref><ref>[http://archive.icann.org/en/tlds/data-escrow-report05mar07.htm ICANN's gTLD Registry Data Escrow Requirements, icann.org]</ref> Both registry and registry escrows follow the same system: a weekly full deposit on Sundays, and a partial deposit on all other days containing all new data since the last full deposit.<ref>[http://www.icann.org/en/resources/registrars/data-escrow/registrar-escrow-08nov01-en.htm Registrar Data Escrow, icann.org]</ref><ref>[http://www.cloudregistry.net/agb/#text/p267 New gTLD Applicant Guidebook]</ref> | ||
==Registry Data Escrow== | ==Registry Data Escrow== | ||
[[File:Data-escrow.gif|thumb|right|Registry data escrow procedures]] | [[File:Data-escrow.gif|thumb|right|Registry data escrow procedures]] | ||
Registry | Registry Data Escrow is one of the essential stakeholder protection mechanisms for gTLDs. Registry Data Escrow ensures that the data associated with registered domain names is never at risk of being lost or inaccessible. Registry Data Escrow is a specialized data protection service designed to meet the compliance and “best practice” needs of domain name registrants worldwide. The service ensures that up-to-date copies of domain name ownership and contact details are held in escrow by a trusted, neutral third party, to be accessed and released only under pre-defined and controlled conditions. The purpose of Registry Data Escrow is to help safeguard registrar and registrant interests in the event of a registry’s business or technical failure.<ref>[http://www.ironmountain.com/Knowledge-Center/Reference-Library/View-by-Document-Type/Data-Sheets-Brochures/R/Registry-Data-Escrow-Data-Sheet.aspx Registry Data Escrow Service, ironmountain.com]</ref> | ||
==History== | ===History=== | ||
The original Registry Agreement, which lasted from 1999-2001, between ICANN and [[Network Solutions]] (and later [[Verisign]]) contained provisions for registry data escrow for the [[.com]], [[.net]], and [[.org]] [[gTLD]]s. In May 2001, ICANN entered into a new Registry Agreement with Verisign for .com, which included expanded escrow provisions. At that time they also entered into separate agreements for [[.org]] and [[.net]]. | The original Registry Agreement, which lasted from 1999-2001, between ICANN and [[Network Solutions]] (and later [[Verisign]]) contained provisions for registry data escrow for the [[.com]], [[.net]], and [[.org]] [[gTLD]]s. In May 2001, ICANN entered into a new Registry Agreement with Verisign for .com, which included expanded escrow provisions. At that time they also entered into separate agreements for [[.org]] and [[.net]]. | ||
In November 2000, ICANN selected seven new gTLDs as part of a proof-of-concept round to expand the Internet | In November 2000, ICANN selected seven new gTLDs as part of a proof-of-concept round to expand the Internet namespace. Registry Agreements for all 7 of these TLDs contained language based on the draft for the 2001 .com agreement with Verisign. These agreements were entered into between 2001 and 2002, beginning with [[.biz]] and [[.info]] in May 2001. | ||
[[Iron Mountain]] was selected in 2001 to serve as ICANN's preferred provider for registry data escrow.<ref>[http://www.ironmountain.com/Services/Technology-Escrow-Services/Domain-Name-Registry-Data-Escrow.aspx Domain Name Registry Data Escrow, icann.org]</ref> | |||
There are currently 4 active versions of the Registry Escrow Agreement. Most gTLDs use Version 1, which is based off of the 2001 .com agreement; Version 2 is used by [[.travel]]; Version 3 by the [[.aero]], [[.coop]], and [[.museum]] [[sTLD|Sponsored TLDs]]; and Version 4 by [[.name]] and [[.pro]]. | |||
Several of the original [[ccTLD]] Sponsorship Agreements and [[MoU]]s also contained provisions for registry escrow. In 2004, however, ICANN moved away from the Sponsorship Agreement and MOU formats, opting for a lightweight Accountability Format, which does not contain detailed provisions for registry escrow, though it does encourage ccTLD managers to operate in a manner compliant to current [[IETF]] standards.<ref>[http://archive.icann.org/en/tlds/data-escrow-report05mar07.htm#Historical ICANN's gTLD Registry Data Escrow Requirements, icann.org]</ref> | |||
==Registrar Data Escrow== | ==Registrar Data Escrow== | ||
| Line 18: | Line 20: | ||
===History=== | ===History=== | ||
Though registrar data escrow was already part of the [[Registrar Accreditation Agreement]], a structured Registrar Data Escrow program was deemed to be necessary by ICANN and a committee of registrars in late 2001. A testbed consisting of a small number of volunteer registrars was conducted prior to the full rollout of the program.<ref>[http://www.icann.org/en/resources/registrars/data-escrow/registrar-escrow-08nov01-en.htm Registrar Data Escrow, icann.org]</ref> | |||
In 2007, however, it came to light that ICANN had not followed through in ensuring that all of its registrars were doing so. After the failure of [[RegisterFly]], the first registrar to go under, thousands of the company's customers lost their domain names or were forced to wait for months until their domains were eventually transferred to [[GoDaddy]]. Following this, ICANN made it a priority to review the RAA and more forcefully implement the Registrar Data Escrow program. [[Iron Mountain]] was selected to implement and execute Registrar Data Escrow.<ref>[http://www.theregister.co.uk/2007/11/29/icann_iron_mountain_data_escrow/ Iron Mountain lands ICANN data escrow agreement, theregister.co.uk]</ref><ref>[http://www.bobparsons.me/archive_article.php?entry_id=147 Go Daddy rescues Registerfly customers, bobparsons.me]</ref> All registrars at that time were expected to enroll in the RDE program within six months.<ref>[http://www.icann.org/en/news/announcements/announcement-2-09nov07-en.htm Implementation of Registrar Data Escrow Program, icann.org]</ref> | |||
==References== | |||
{{reflist}} | |||
[[Category: Glossary]] | [[Category: Glossary]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:41, 5 March 2021
Data Escrow is the act of storing data with a neutral third party[1] in case of registry or registrar failure, accreditation termination, or accreditation relapse without renewal. ICANN requires all registrars and gTLD registries to contract with a data escrow provider in order to safeguard registrants.[2][3] Both registry and registry escrows follow the same system: a weekly full deposit on Sundays, and a partial deposit on all other days containing all new data since the last full deposit.[4][5]
Registry Data Escrow[edit | edit source]
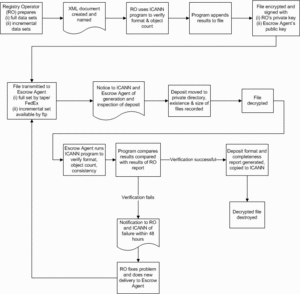
Registry Data Escrow is one of the essential stakeholder protection mechanisms for gTLDs. Registry Data Escrow ensures that the data associated with registered domain names is never at risk of being lost or inaccessible. Registry Data Escrow is a specialized data protection service designed to meet the compliance and “best practice” needs of domain name registrants worldwide. The service ensures that up-to-date copies of domain name ownership and contact details are held in escrow by a trusted, neutral third party, to be accessed and released only under pre-defined and controlled conditions. The purpose of Registry Data Escrow is to help safeguard registrar and registrant interests in the event of a registry’s business or technical failure.[6]
History[edit | edit source]
The original Registry Agreement, which lasted from 1999-2001, between ICANN and Network Solutions (and later Verisign) contained provisions for registry data escrow for the .com, .net, and .org gTLDs. In May 2001, ICANN entered into a new Registry Agreement with Verisign for .com, which included expanded escrow provisions. At that time they also entered into separate agreements for .org and .net.
In November 2000, ICANN selected seven new gTLDs as part of a proof-of-concept round to expand the Internet namespace. Registry Agreements for all 7 of these TLDs contained language based on the draft for the 2001 .com agreement with Verisign. These agreements were entered into between 2001 and 2002, beginning with .biz and .info in May 2001.
Iron Mountain was selected in 2001 to serve as ICANN's preferred provider for registry data escrow.[7]
There are currently 4 active versions of the Registry Escrow Agreement. Most gTLDs use Version 1, which is based off of the 2001 .com agreement; Version 2 is used by .travel; Version 3 by the .aero, .coop, and .museum Sponsored TLDs; and Version 4 by .name and .pro.
Several of the original ccTLD Sponsorship Agreements and MoUs also contained provisions for registry escrow. In 2004, however, ICANN moved away from the Sponsorship Agreement and MOU formats, opting for a lightweight Accountability Format, which does not contain detailed provisions for registry escrow, though it does encourage ccTLD managers to operate in a manner compliant to current IETF standards.[8]
Registrar Data Escrow[edit | edit source]
The Registrar Data Escrow program was initiated by ICANN to protect data associated with registered domain names in a secure escrow environment.
History[edit | edit source]
Though registrar data escrow was already part of the Registrar Accreditation Agreement, a structured Registrar Data Escrow program was deemed to be necessary by ICANN and a committee of registrars in late 2001. A testbed consisting of a small number of volunteer registrars was conducted prior to the full rollout of the program.[9]
In 2007, however, it came to light that ICANN had not followed through in ensuring that all of its registrars were doing so. After the failure of RegisterFly, the first registrar to go under, thousands of the company's customers lost their domain names or were forced to wait for months until their domains were eventually transferred to GoDaddy. Following this, ICANN made it a priority to review the RAA and more forcefully implement the Registrar Data Escrow program. Iron Mountain was selected to implement and execute Registrar Data Escrow.[10][11] All registrars at that time were expected to enroll in the RDE program within six months.[12]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Guard-It.com FAQs or EscrowTech International, Inc.
- ↑ Implementation of Registrar Data Escrow Program, icann.org
- ↑ ICANN's gTLD Registry Data Escrow Requirements, icann.org
- ↑ Registrar Data Escrow, icann.org
- ↑ New gTLD Applicant Guidebook
- ↑ Registry Data Escrow Service, ironmountain.com
- ↑ Domain Name Registry Data Escrow, icann.org
- ↑ ICANN's gTLD Registry Data Escrow Requirements, icann.org
- ↑ Registrar Data Escrow, icann.org
- ↑ Iron Mountain lands ICANN data escrow agreement, theregister.co.uk
- ↑ Go Daddy rescues Registerfly customers, bobparsons.me
- ↑ Implementation of Registrar Data Escrow Program, icann.org
