Internet: Difference between revisions
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
===United States=== | ===United States=== | ||
To counteract the perceived threat of Russian space exploration during the Cold War, the United States boosted investment in research and computer science. Fearing the potential destruction of the national telephone line network, the United States turned to J.C.R. Licklider, a psychologist and computer scientist at MIT and DARPA to develop a robust | To counteract the perceived threat of Russian space exploration during the Cold War, the United States boosted investment in research and computer science. Fearing the potential destruction of the national telephone line network, the United States turned to J.C.R. Licklider, a psychologist and computer scientist at MIT and DARPA to develop a robust, defensive alternative.<ref name="Invention of Internet">http://www.history.com/topics/inventions/invention-of-the-internet The Invention of the Internet. History.com Staff. History.com. 20 Mar 2015</ref> | ||
Beginning in 1962, Licklider strengthened his "Galactic Network" idea, which included an expansive network of computers that would offer its users access to data and programs from a series of sites. After becoming the first head of [[DARPA]]'s computer research program in October 1962, Licklider successfully convinced his colleagues of the vision's merit. | Beginning in 1962, Licklider strengthened his "Galactic Network" idea, which included an expansive network of computers that would offer its users access to data and programs from a series of sites. After becoming the first head of [[DARPA]]'s computer research program in October 1962, Licklider successfully convinced his colleagues of the vision's merit. | ||
Concurrently, [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leonard_Kleinrock Leonard Kleinrock] pursued the feasibility of [[packet switching]], a method of delivery that sends information in small packets, or portions through different routes as a part of his doctoral research. This idea was a central component of the mechanics of the Internet. | Concurrently, [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leonard_Kleinrock Leonard Kleinrock] pursued the feasibility of [[packet switching]], a method of delivery that sends information in small packets, or portions through different routes as a part of his doctoral research. This idea was a central component of the mechanics of the Internet. | ||
Revision as of 22:18, 27 March 2015
UNDER CONSTRUCTION
The term Internet is used to describe the interconnected servers, computers, and networks that work through a standard protocol and provide the structure for information to be accessed on "The Web." In popular culture, the terms "Internet" and "Web" are sometimes used interchangeably to refer to the publicly-accessible websites and servers that can be reached using a Web browser. The Internet gives its users global broadcasting abilities, access to and the ability to add to world knowledge, as well as make it possible for collaboration regardless of location. [1]
History[edit | edit source]
United States[edit | edit source]
To counteract the perceived threat of Russian space exploration during the Cold War, the United States boosted investment in research and computer science. Fearing the potential destruction of the national telephone line network, the United States turned to J.C.R. Licklider, a psychologist and computer scientist at MIT and DARPA to develop a robust, defensive alternative.[2] Beginning in 1962, Licklider strengthened his "Galactic Network" idea, which included an expansive network of computers that would offer its users access to data and programs from a series of sites. After becoming the first head of DARPA's computer research program in October 1962, Licklider successfully convinced his colleagues of the vision's merit. Concurrently, Leonard Kleinrock pursued the feasibility of packet switching, a method of delivery that sends information in small packets, or portions through different routes as a part of his doctoral research. This idea was a central component of the mechanics of the Internet.
ARPANET[edit | edit source]
The Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) was a branch of the United State's military and earliest iteration of the Internet. It used a packet-switching method to transmit information between various 'nodes' across the country. It was the first network to use TCP/IP, developed by Vint Cerf and Robert Kahn.
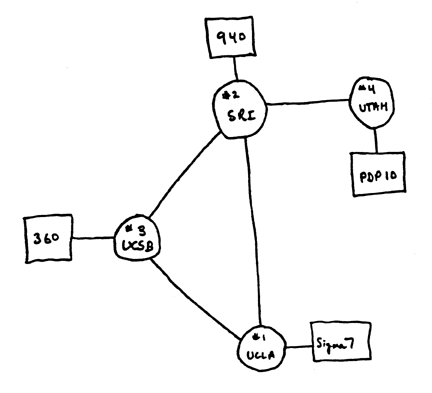
Nodes were delegated individually to different campuses located in Western and Northeastern United States. This process began in 1969 when BBN, a research and development firm based in Cambridge, Massachusetts, delivered the first Interface Message Processor, or IMP[3] to Kleinrock at UCLA. Here, graduate students Vinton Cerf, Steve Crocker, Bill Naylor, John Postel and Mike Wingfield worked to connect their node by hardware with their IMP. The work was a success and messages between the two machines passed without interference.
Researchers at Doug Engelbert's Stanford Research Institute (SRI) were next to receive an IMP. Upon receipt, members at UCLA and Stanford conducted the first network inter-nodal communication. Using a low-speed dial-up line, the researchers developed a connection, testing the packet transmission. The experiment was a minor success, scientists in Stanford received the 'L' and 'O' of 'LOGIN', and the transmission crashed ARPA's fragile network. Regardless of its initial gaps, the "packet-switching" communication test proved to be instrumental in the formation of ARPANET. [1]
Other deliveries to campuses followed shortly, and are included below:
ARPANET Nodes
- Network Measurement Center at UCLA, led by Kleinrock
- Stanford Research Institute (SRI), led by Doug Engelbert
- Network Information Center, led by Elizabeth J. Feinler
- UC Santa Barbara
- University of Utah
ARPANET Email[edit | edit source]
The first public demonstration of ARPANET's capabilities was at the International Computer Communication Conference in October, 1972. This exhibition is thought to have inspired confidence in developing network technologies and support for further development. [4] In May of that year, Ray Tomlinson completed programming an application that would allow inter-network messaging, from user to user. The program expanded, giving users the ability to not only read messages, but file, forward and respond directly to messages. [2]
Beyond ARPANET, 1973[edit | edit source]
Having secured ARPANET's closed network, Robert Kahn and Vinton Cerf collaborated on connecting multiple networks. This project later transitioned into Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and would allow multiple networks to interact and stand alone with security separate from their interconnected family. This would also allow a decentralized approach to managing networks.
In the same year ARPANET made its first international connections to the University College of London and the Royal Radar Establishment of Norway. [4]
ICANN[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 http://www.internetsociety.org/sites/default/files/Brief_History_of_the_Internet.pdf A Brief History of the Internet. Leiner, Cerf, Clark, Kahn, Kleinrock, Lynch, Postel, Roberts, Wolff. Internet Society. 19 Mar 2015
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 http://www.history.com/topics/inventions/invention-of-the-internet The Invention of the Internet. History.com Staff. History.com. 20 Mar 2015
- ↑ http://www.livinginternet.com/i/ii_arpanet.htm. Michael Hauben. Retrieved 26 Mar 2015
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 http://www.newmedia.org/history-of-the-internet.html?page=2 The New Media Institute. 20 Mar 2015