IDN ccTLD: Difference between revisions
Created page with "Internationalized Domain Name (IDN) ccTLDs are encoded domain names assigned to countries or geographic regions that are displayed in an end-user application in their language..." |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Internationalized Domain Name (IDN) ccTLDs are encoded domain names assigned to countries or geographic regions that are displayed in an end-user application in their language-native script or alphabet, such as Arabic, or a non-alphabetic writing system, such as Chinese characters. Although the IDN class uses the term code, some of the ccTLDs are full words. | Internationalized Domain Name (IDN) ccTLDs are encoded domain names assigned to countries or geographic regions that are displayed in an end-user application in their language-native script or alphabet, such as Arabic, or a non-alphabetic writing system, such as Chinese characters. Although the IDN class uses the term code, some of the ccTLDs are full words. | ||
==History of IDN Fast Track== | ==History of IDN Fast Track Process== | ||
At its Seoul conference in 2009, [[ICANN]] approved the [[IDN]] [[ccTLD]] Fast Track process, which allowed [[ccTLD]]s to be written in non-Latin characters. The IDN ccTLD Fast Track Process was launched on 16 November 2009. Eligible countries and territories were able to request their respective IDN ccTLD(s) through the process.<ref>[https://www.icann.org/resources/pages/fast-track-2012-02-25-en Fast Track Process]</ref> | [[File:Idn-cctld-strings-720x540-18may20-en.png|500px|thumbnail|right|Successful IDN ccTLD applications as of May 2020 (Image from ICANN.org]]At its Seoul conference in 2009, [[ICANN]] approved the [[IDN]] [[ccTLD]] Fast Track process, which allowed [[ccTLD]]s to be written in non-Latin characters. The IDN ccTLD Fast Track Process was launched on 16 November 2009. Eligible countries and territories were able to request their respective IDN ccTLD(s) through the process.<ref>[https://www.icann.org/resources/pages/fast-track-2012-02-25-en Fast Track Process]</ref> | ||
The process entailed three steps: | '''The process entailed three steps:''' | ||
#Preparations in country/territory | #Preparations in country/territory | ||
#String Evaluation | #String Evaluation | ||
Revision as of 19:33, 19 February 2021
Internationalized Domain Name (IDN) ccTLDs are encoded domain names assigned to countries or geographic regions that are displayed in an end-user application in their language-native script or alphabet, such as Arabic, or a non-alphabetic writing system, such as Chinese characters. Although the IDN class uses the term code, some of the ccTLDs are full words.
History of IDN Fast Track Process[edit | edit source]
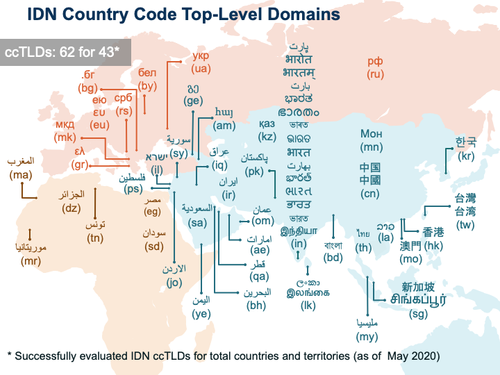
At its Seoul conference in 2009, ICANN approved the IDN ccTLD Fast Track process, which allowed ccTLDs to be written in non-Latin characters. The IDN ccTLD Fast Track Process was launched on 16 November 2009. Eligible countries and territories were able to request their respective IDN ccTLD(s) through the process.[1]
The process entailed three steps:
- Preparations in country/territory
- String Evaluation
- String Delegation
Russia, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates were some of the first countries to advance in the application and implementation process.[2]
