Supply Chain Attack: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Recent Attacks== | ==Recent Attacks== | ||
Recently, criminals have targeted the following software vendors and IT services companies to infect their clients: | Recently, criminals have targeted the following software vendors and IT services companies to infect their clients: | ||
'''Kaseya''' <br/> | |||
On July 2, hackers breached this Florida-based IT management software company. Kaseya specializes in monitoring and controlling the computer networks of “managed service providers” that sell their IT and cybersecurity services to hundreds of thousands of small- and medium-sized businesses. After the hackers infected 50 of Kaseya's managed service providers, they were able to enter the systems of those companies' 1,500 clients. The hackers encrypted the victims’ data and demanded US$50 million in exchange for the key.<ref>[https://qz.com/2030053/what-is-a-supply-chain-cyber-attack/ What is a supply chain attack, Quartz]</ref> | On July 2, hackers breached this Florida-based IT management software company. Kaseya specializes in monitoring and controlling the computer networks of “managed service providers” that sell their IT and cybersecurity services to hundreds of thousands of small- and medium-sized businesses. After the hackers infected 50 of Kaseya's managed service providers, they were able to enter the systems of those companies' 1,500 clients. The hackers encrypted the victims’ data and demanded US$50 million in exchange for the key.<ref>[https://qz.com/2030053/what-is-a-supply-chain-cyber-attack/ What is a supply chain attack, Quartz]</ref> <br/> | ||
[[SolarWinds]] | |||
''SunBurst Attack'' <br/> | |||
SolarWinds customers experienced a Russian-state-sponsored cyberattack that inserted a vulnerability called Sunburst into the Orion Platform (versions 2019.4 HF 5, 2020.2 unpatched, and 2020.2 HF 1). It allowed the attackers to compromise the servers running Orion products. The code was used in a targeted way to the extent that its exploitation required manual intervention. SolarWinds worked with [CrowdStrike]] and [[KPMG]] to identify a component of Sunburst called Sunspot, which was responsible for injecting the Sunburst malicious code into the Orion Platform during the build process. Other components of the Sunburst malware chain include Teardrop and Raindrop.<ref>[https://www.solarwinds.com/sa-overview/securityadvisory#anchor2 Security Advisor, SolarWinds]</ref> | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 12:48, 26 July 2021
A Supply Chain Attack is when a threat actor makes use of unsecured network protocols, unprotected server infrastructures, or unsafe coding practices. The supply chain attacker breaks in, changes source codes, and hides malware in build and update processes.[1]
Recent Attacks
Recently, criminals have targeted the following software vendors and IT services companies to infect their clients:
Kaseya
On July 2, hackers breached this Florida-based IT management software company. Kaseya specializes in monitoring and controlling the computer networks of “managed service providers” that sell their IT and cybersecurity services to hundreds of thousands of small- and medium-sized businesses. After the hackers infected 50 of Kaseya's managed service providers, they were able to enter the systems of those companies' 1,500 clients. The hackers encrypted the victims’ data and demanded US$50 million in exchange for the key.[2]
SolarWinds
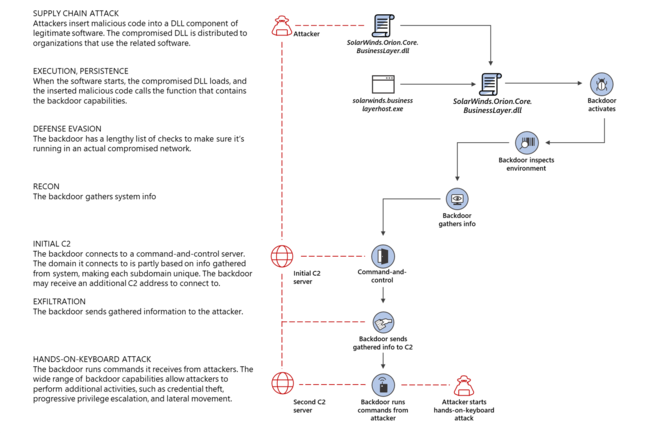
SunBurst Attack
SolarWinds customers experienced a Russian-state-sponsored cyberattack that inserted a vulnerability called Sunburst into the Orion Platform (versions 2019.4 HF 5, 2020.2 unpatched, and 2020.2 HF 1). It allowed the attackers to compromise the servers running Orion products. The code was used in a targeted way to the extent that its exploitation required manual intervention. SolarWinds worked with [CrowdStrike]] and KPMG to identify a component of Sunburst called Sunspot, which was responsible for injecting the Sunburst malicious code into the Orion Platform during the build process. Other components of the Sunburst malware chain include Teardrop and Raindrop.[3]
