Cybersecurity: Difference between revisions
m added Category:Articles to be expanded using HotCat |
|||
| (20 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Cybersecurity''' is the practice of protecting systems, networks, and programs from digital attacks. Cyberattacks usually seek to access, change, or destroy sensitive information; extort money from their victims; or disrupt business as usual.<ref>[https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/security/what-is-cybersecurity.html#~types-of-threats What is Cybersecurity, Cisco]</ref> Implementing cybersecurity measures is challenging because it is a cat-and-mouse game, and today there are more devices than people. | '''Cybersecurity''' is the practice of protecting systems, networks, and programs from digital attacks. Cyberattacks usually seek to access, change, or destroy sensitive information; extort money from their victims; or disrupt business as usual.<ref>[https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/security/what-is-cybersecurity.html#~types-of-threats What is Cybersecurity, Cisco]</ref> Implementing cybersecurity measures is challenging because it is a cat-and-mouse game, and today there are more devices than people. | ||
Ensuring the cybersecurity of computers, networks, programs, and data relies on multiple layers of protection involving the detection, investigation, and remediation of threats. Users need to understand and comply with basic data security principles like choosing strong passwords, being wary of attachments in email, and backing up data. However, many questions remain over whether people can outsmart [[Social Engineering Attacks]]. Common technology used to protect endpoint devices | Ensuring the cybersecurity of computers, networks, programs, and data relies on multiple layers of protection involving the detection, investigation, and remediation of threats. Users need to understand and comply with basic data security principles like choosing strong passwords, being wary of attachments in email, and backing up data. However, many questions remain over whether people can outsmart [[Social Engineering Attacks]]. Common technology used to protect endpoint devices (such as computers, smart devices, and routers), networks, and clouds include firewalls, DNS filtering, malware protection, antivirus software, and email security. | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
* | *From the late 1950s through the 1970s, [[Phone Phreaking]] marked the beginning of present-day hacking culture; simple security tools, such as access controls and passwords, were implemented. Then came cryptographic applications, such as public-key cryptography, security verification, cryptographic protocols, and cryptographic hashing.<ref>[https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167404817302249?casa_token=deFBX0B2eLMAAAAA:FXPmbrKThtFL1_aSpVTABhyEzhWMiQhyk3wXhXfX5WOewf7FSM9gEHvkYN_TNgqVbn5kJw5pl7Q Hatfield, Joseph.2018. "Social engineering in cybersecurity." ''Computers & Security'', 73:102-113]</ref> | ||
* | *In 1983, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology was granted the first US patent for a cryptographic communication system. | ||
*By 1990, [[Malware]], malware detection, antivirus techniques, buffer overflow attacks, intrusion detection, and firewalls were in play.<ref>P.J. & D.E. Denning. | *By 1990, [[Malware]], malware detection, antivirus techniques, buffer overflow attacks, intrusion detection, and firewalls were in play.<ref>P.J. & D.E. Denning.2016."Cybersecurity is harder than building bridges."''Am Sci'', 104(3):1-6</ref> | ||
Am Sci, 104(3):1-6</ref> | *By 2006, automated vigilance had become more-or-less the norm, leading Greiner to call [[Social Engineering Attacks]] "the highest form of hacking."<ref>L. Greiner.2006." | ||
Hacking your network's weakest link – you" ''Netw Mag'', 12(1):9-12</ref> | |||
*In the 2010s, cybersecurity went mainstream: most corporations had to say (if not do) something about client privacy and data security.<ref>[https://www.forbes.com/sites/forrester/2019/12/18/decade-retrospective-cybersecurity-from-2010-to-2019/?sh=60d1b05d4d51 Decade Retrospective, Cybersecurity, Forbes]</ref> | |||
*In 2011, researchers at Lockheed Martin standardized cybersecurity jargon with their [https://www.lockheedmartin.com/en-us/capabilities/cyber/cyber-kill-chain.html Cyber Kill Chain] model, published in their white paper, "Intelligence-Driven Computer Network Defense Informed by Analysis of Adversary Campaigns and Intrusion Kill Chains."<ref>[https://www.lockheedmartin.com/content/dam/lockheed-martin/rms/documents/cyber/LM-White-Paper-Intel-Driven-Defense.pdf Eric M. Hutchins, Michael J. Cloppert, & Rohan M. Amin.2011."Lockheed Martin Kill Chain.]</ref> | |||
*In 2013, nonspecialists became more aware of nation-state cyberattacks with Mandiant's release of the [https://www.mandiant.com/resources/apt1-exposing-one-of-chinas-cyber-espionage-units APT1 Report], which outlined how China was able to quickly steal intellectual property from US firms. | |||
*In 2014, [[NIST]] released its first cybersecurity framework, which conceptualized how to identify, protect, detect, respond, and recover from attacks.<ref>[https://www.nist.gov/cyberframework Cyberframework, NIST]</ref> | |||
*In 2022, [[Peiter Zatko]], aka Mudge, former chief security officer at [[Twitter]], blew the whistle on his ex-employer's extensive cybersecurity vulnerabilities, including allowing too many of its staff access to the platform's central controls and most sensitive information without adequate oversight, with one or more such employees working for a foreign intelligence service; misleading its own board and government regulators; opening the door to foreign spying or manipulation, hacking and disinformation campaigns; not deleting users' data after they cancel their accounts; not understanding/reporting the true number of bots on the platform.<ref>[https://www.cnn.com/2022/08/23/tech/twitter-whistleblower-peiter-zatko-security/index.html Ex-Twitter exec blows the whistle, alleging reckless and negligent cybersecurity policies, CNN Business]</ref> | |||
==Government Involvement== | ==Tools & Techniques== | ||
* Artificial Intelligence | |||
* Machine Learning | |||
* [[MITRE ATT&CK]] | |||
* Red Teams | |||
* Blue Teams | |||
* Purple Teams | |||
** Threat Informed Defense<ref>[https://ctid.mitre-engenuity.org/our-work/ Our Work, CTID, Mitre Engenuity]</ref> | |||
==Sectors== | |||
===Government Involvement=== | |||
Government leaders have different understandings and expectations of how involved a government should be in a nation’s cybersecurity. | Government leaders have different understandings and expectations of how involved a government should be in a nation’s cybersecurity. | ||
McKinsey suggests considering several questions to ascertain a government’s role in cybersecurity.<ref>[https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/public-and-social-sector/our-insights/asking-the-right-questions-to-define-governments-role-in-cybersecurity# Defining Govts' Role in Cybersecurity, McKinsey]</ref> | McKinsey suggests considering several questions to ascertain a government’s role in cybersecurity.<ref>[https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/public-and-social-sector/our-insights/asking-the-right-questions-to-define-governments-role-in-cybersecurity# Defining Govts' Role in Cybersecurity, McKinsey]</ref> | ||
| Line 21: | Line 36: | ||
#*Australia introduced a notifiable-data-breaches scheme in 2017, making it a legal requirement to notify affected individuals and the Office of the Australian Information Commissioner of serious data breaches. | #*Australia introduced a notifiable-data-breaches scheme in 2017, making it a legal requirement to notify affected individuals and the Office of the Australian Information Commissioner of serious data breaches. | ||
# Relationship with the private and academic sectors? | # Relationship with the private and academic sectors? | ||
#*Singapore’s National Cybersecurity R&D Programme supports | #*Singapore’s National Cybersecurity R&D Programme supports public-private research partnerships and budgeted $190 million Singapore dollars ($137.85 million) in the national strategy for the creation of the National Cybersecurity R&D Laboratory at the National University of Singapore. | ||
# How does it define national critical infrastructure? | # How does it define national critical infrastructure? | ||
#*In the United States, the Department of Homeland Security coordinates a national infrastructure-protection plan and requires sector-specific agencies, such as the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) to develop sector-specific plans. | #*In the United States, the Department of Homeland Security coordinates a national infrastructure-protection plan and requires sector-specific agencies, such as the [[Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency]] (CISA) to develop sector-specific plans. | ||
===The Industry=== | |||
When the development for computers expanded from bureaucratic firms to daily use for the public, some companies were developed along the way to protect their devices from malware and vulnerabilities especially for those using Microsoft based product. The work for cybersecurity started to be adopted by ISPs where for some known websites are blocked when an individual sends a request to a website and this is usually done by monitoring cybercrimes from a particular service or checking [[SSL Certificate|secure socket layer certificate]] for the website. The web hosting industry have been doing many additional research to protect their servers and clients which up to date there are still weaknesses that this industry suffers from time to time, AWS is one of the popular service that it focused on cybersecurity and legitimacy for clients and businesses. | |||
===Providers=== | ===Providers=== | ||
[[File:Billion-dollar cybersecurity exits, CB Insights.png|655px|right|(CB Insights)]]In the past decade, two dozen cybersecurity startups have attained IPO or M&A values of $1 billion; 10 of them since 2017.<ref>[https://www.cbinsights.com/research/cybersecurity-billion-dollar-exits-infographic/ Cybersecurity Exits, CB Insights]</ref> | [[File:Billion-dollar cybersecurity exits, CB Insights.png|655px|right|(CB Insights)]]In the past decade, two dozen [[:Category:Cybersecurity Providers|cybersecurity startups]] have attained IPO or M&A values of at least US$1 billion; 10 of them since 2017.<ref>[https://www.cbinsights.com/research/cybersecurity-billion-dollar-exits-infographic/ Cybersecurity Exits, CB Insights]</ref> | ||
===Clients=== | ===Clients=== | ||
PwC conducted a survey in 2020 and released it as “Global Digital Trust Insights 2021.” They asked 3,249 business and technology executives about their CISOs and the present and future of cybersecurity.<ref>[https://www.pwc.com/us/en/services/consulting/cybersecurity/library/assets/pwc-2021-global-digital-trust-insights.pdf Trust Insights, PwC]</ref> Some of their findings included: | PwC conducted a survey in 2020 and released it as “Global Digital Trust Insights 2021.” They asked 3,249 business and technology executives about their CISOs and the present and future of cybersecurity.<ref>[https://www.pwc.com/us/en/services/consulting/cybersecurity/library/assets/pwc-2021-global-digital-trust-insights.pdf Trust Insights, PwC]</ref> Some of their findings included: | ||
| Line 34: | Line 50: | ||
*More (55%) are increasing cyber budgets than decreasing them in 2021. | *More (55%) are increasing cyber budgets than decreasing them in 2021. | ||
*However, most executives lack confidence that their cybersecurity budgets align with the most significant risks. | *However, most executives lack confidence that their cybersecurity budgets align with the most significant risks. | ||
===Key Figures=== | |||
Some of the people who have significantly shaped the industry include:<ref>[https://securitytrails.com/blog/cybersecurity-legends-famous-hackers Cybersecurity Legends, Security Trails]</ref> | |||
* [[Allen Paller]] | |||
* [[Kevin Mitnick]] | |||
* [[Kevin Poulsen]] | |||
* [[Robert Tappan Morris]] | |||
* [[Troy Hunt]] | |||
* [[Brian Krebs]] | |||
* [[John McAfee]] | |||
* [[Eugene Kaspersky]] | |||
* [[Charlie Alfred Miller]] | |||
* [[Ginni Rometty]] | |||
* [[Dan Kaminsky]] | |||
* [[Mudge]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
[[Category:Articles to be expanded]] | |||
Latest revision as of 00:55, 3 April 2024
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting systems, networks, and programs from digital attacks. Cyberattacks usually seek to access, change, or destroy sensitive information; extort money from their victims; or disrupt business as usual.[1] Implementing cybersecurity measures is challenging because it is a cat-and-mouse game, and today there are more devices than people.
Ensuring the cybersecurity of computers, networks, programs, and data relies on multiple layers of protection involving the detection, investigation, and remediation of threats. Users need to understand and comply with basic data security principles like choosing strong passwords, being wary of attachments in email, and backing up data. However, many questions remain over whether people can outsmart Social Engineering Attacks. Common technology used to protect endpoint devices (such as computers, smart devices, and routers), networks, and clouds include firewalls, DNS filtering, malware protection, antivirus software, and email security.
History
- From the late 1950s through the 1970s, Phone Phreaking marked the beginning of present-day hacking culture; simple security tools, such as access controls and passwords, were implemented. Then came cryptographic applications, such as public-key cryptography, security verification, cryptographic protocols, and cryptographic hashing.[2]
- In 1983, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology was granted the first US patent for a cryptographic communication system.
- By 1990, Malware, malware detection, antivirus techniques, buffer overflow attacks, intrusion detection, and firewalls were in play.[3]
- By 2006, automated vigilance had become more-or-less the norm, leading Greiner to call Social Engineering Attacks "the highest form of hacking."[4]
- In the 2010s, cybersecurity went mainstream: most corporations had to say (if not do) something about client privacy and data security.[5]
- In 2011, researchers at Lockheed Martin standardized cybersecurity jargon with their Cyber Kill Chain model, published in their white paper, "Intelligence-Driven Computer Network Defense Informed by Analysis of Adversary Campaigns and Intrusion Kill Chains."[6]
- In 2013, nonspecialists became more aware of nation-state cyberattacks with Mandiant's release of the APT1 Report, which outlined how China was able to quickly steal intellectual property from US firms.
- In 2014, NIST released its first cybersecurity framework, which conceptualized how to identify, protect, detect, respond, and recover from attacks.[7]
- In 2022, Peiter Zatko, aka Mudge, former chief security officer at Twitter, blew the whistle on his ex-employer's extensive cybersecurity vulnerabilities, including allowing too many of its staff access to the platform's central controls and most sensitive information without adequate oversight, with one or more such employees working for a foreign intelligence service; misleading its own board and government regulators; opening the door to foreign spying or manipulation, hacking and disinformation campaigns; not deleting users' data after they cancel their accounts; not understanding/reporting the true number of bots on the platform.[8]
Tools & Techniques
- Artificial Intelligence
- Machine Learning
- MITRE ATT&CK
- Red Teams
- Blue Teams
- Purple Teams
- Threat Informed Defense[9]
Sectors
Government Involvement
Government leaders have different understandings and expectations of how involved a government should be in a nation’s cybersecurity. McKinsey suggests considering several questions to ascertain a government’s role in cybersecurity.[10]
- Who is accountable?
- Some national and state governments have consolidated accountabilities into a clear structure, such as Estonia’s Cyber Security Council, or have crisis-response mechanisms as in Sweden.
- Germany has its Bundesamt für Sicherheit in der Informationstechnik (Federal Office for Information Security).
- The United Kingdom’s National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) has been cited as a model for government-level cybersecurity.
- How centralized is it?
- Japan’s Cyber Security Strategic Headquarters hosts audit and regulation functions in a centralized agency as does Romania’s Association for Information Security Assurance.
- India has dispersed audit functions across multiple bodies.
- Australia introduced a notifiable-data-breaches scheme in 2017, making it a legal requirement to notify affected individuals and the Office of the Australian Information Commissioner of serious data breaches.
- Relationship with the private and academic sectors?
- Singapore’s National Cybersecurity R&D Programme supports public-private research partnerships and budgeted $190 million Singapore dollars ($137.85 million) in the national strategy for the creation of the National Cybersecurity R&D Laboratory at the National University of Singapore.
- How does it define national critical infrastructure?
- In the United States, the Department of Homeland Security coordinates a national infrastructure-protection plan and requires sector-specific agencies, such as the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) to develop sector-specific plans.
The Industry
When the development for computers expanded from bureaucratic firms to daily use for the public, some companies were developed along the way to protect their devices from malware and vulnerabilities especially for those using Microsoft based product. The work for cybersecurity started to be adopted by ISPs where for some known websites are blocked when an individual sends a request to a website and this is usually done by monitoring cybercrimes from a particular service or checking secure socket layer certificate for the website. The web hosting industry have been doing many additional research to protect their servers and clients which up to date there are still weaknesses that this industry suffers from time to time, AWS is one of the popular service that it focused on cybersecurity and legitimacy for clients and businesses.
Providers
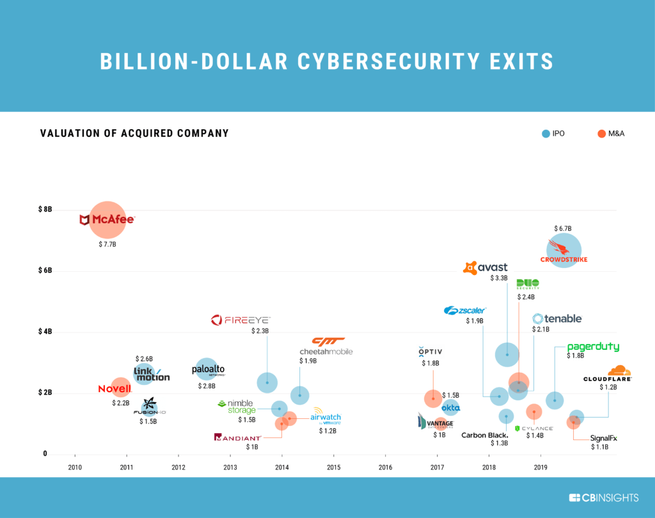
In the past decade, two dozen cybersecurity startups have attained IPO or M&A values of at least US$1 billion; 10 of them since 2017.[11]
Clients
PwC conducted a survey in 2020 and released it as “Global Digital Trust Insights 2021.” They asked 3,249 business and technology executives about their CISOs and the present and future of cybersecurity.[12] Some of their findings included:
- Nearly all (96%) say they would adjust their cybersecurity strategy due to COVID-19.
- Half are more likely now to consider cybersecurity in every business decision, up from 25% in 2019.
- More (55%) are increasing cyber budgets than decreasing them in 2021.
- However, most executives lack confidence that their cybersecurity budgets align with the most significant risks.
Key Figures
Some of the people who have significantly shaped the industry include:[13]
- Allen Paller
- Kevin Mitnick
- Kevin Poulsen
- Robert Tappan Morris
- Troy Hunt
- Brian Krebs
- John McAfee
- Eugene Kaspersky
- Charlie Alfred Miller
- Ginni Rometty
- Dan Kaminsky
- Mudge
References
- ↑ What is Cybersecurity, Cisco
- ↑ Hatfield, Joseph.2018. "Social engineering in cybersecurity." Computers & Security, 73:102-113
- ↑ P.J. & D.E. Denning.2016."Cybersecurity is harder than building bridges."Am Sci, 104(3):1-6
- ↑ L. Greiner.2006." Hacking your network's weakest link – you" Netw Mag, 12(1):9-12
- ↑ Decade Retrospective, Cybersecurity, Forbes
- ↑ Eric M. Hutchins, Michael J. Cloppert, & Rohan M. Amin.2011."Lockheed Martin Kill Chain.
- ↑ Cyberframework, NIST
- ↑ Ex-Twitter exec blows the whistle, alleging reckless and negligent cybersecurity policies, CNN Business
- ↑ Our Work, CTID, Mitre Engenuity
- ↑ Defining Govts' Role in Cybersecurity, McKinsey
- ↑ Cybersecurity Exits, CB Insights
- ↑ Trust Insights, PwC
- ↑ Cybersecurity Legends, Security Trails
