MITRE ATT&CK: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''MITRE ATT&CK''' is a free framework that outlines all of the possible approaches cyber threat actors make take. The knowledge base, which is based entirely on real-world observations, offers a foundation for the development of specific threat models and methodologies for private, government, and [[Cybersecurity]] sectors.<ref>[https://attack.mitre.org/ About MITRE Attack, MITRE]</ref> The framework has one component for enterprise IT networks and clouds, and another for mobile devices. | '''MITRE ATT&CK''' is a free framework that outlines all of the possible approaches cyber threat actors make take. The knowledge base, which is based entirely on real-world observations, offers a foundation for the development of specific threat models and methodologies for private, government, and [[Cybersecurity]] sectors.<ref>[https://attack.mitre.org/ About MITRE Attack, MITRE]</ref> The framework has one component for enterprise IT networks and clouds, and another for mobile devices. | ||
ATT&CK stands for Adversarial Tactics, Techniques, and Common Knowledge. There are different matrices of cyberattack techniques, sorted by tactics, for Windows, Linux, Mac, and mobile systems. The teams that use the ATT&CK model can document and track what threat actors are doing at the various stages of a cyberattack to infiltrate the network and exfiltrate data.<ref>[https://www.varonis.com/blog/mitre-attck-framework-complete-guide/ ATT&CK Complete Guide, Varonis]</ref> ATT&CK can be used to run an adversary emulation, which is the process of assessing the security of a technology domain by applying cyber threat intelligence about specific adversaries to verify an organization's capacity to detect and mitigate adversarial activity. | ATT&CK stands for Adversarial Tactics, Techniques, and Common Knowledge. There are different matrices of cyberattack techniques, sorted by tactics, for Windows, Linux, Mac, and mobile systems. The teams that use the ATT&CK model can document and track what threat actors are doing at the various stages of a cyberattack to infiltrate the network and exfiltrate data.<ref>[https://www.varonis.com/blog/mitre-attck-framework-complete-guide/ ATT&CK Complete Guide, Varonis]</ref> ATT&CK can be used to run an adversary emulation, which is the process of assessing the security of a technology domain by applying cyber threat intelligence about specific adversaries to verify an organization's capacity to detect and mitigate adversarial activity. It can also be used for red teaming, which is an exercise in completing a breach without being detected.<ref>[https://attack.mitre.org/docs/ATTACK_Design_and_Philosophy_March_2020.pdf ATT&CK Design and Philosophy, MITRE 2020]</ref> | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
Revision as of 17:18, 9 August 2021
MITRE ATT&CK is a free framework that outlines all of the possible approaches cyber threat actors make take. The knowledge base, which is based entirely on real-world observations, offers a foundation for the development of specific threat models and methodologies for private, government, and Cybersecurity sectors.[1] The framework has one component for enterprise IT networks and clouds, and another for mobile devices. ATT&CK stands for Adversarial Tactics, Techniques, and Common Knowledge. There are different matrices of cyberattack techniques, sorted by tactics, for Windows, Linux, Mac, and mobile systems. The teams that use the ATT&CK model can document and track what threat actors are doing at the various stages of a cyberattack to infiltrate the network and exfiltrate data.[2] ATT&CK can be used to run an adversary emulation, which is the process of assessing the security of a technology domain by applying cyber threat intelligence about specific adversaries to verify an organization's capacity to detect and mitigate adversarial activity. It can also be used for red teaming, which is an exercise in completing a breach without being detected.[3]
History
In 2013, the Mitre Corporation, an American nonprofit managing federally funded research and development centers, started ATT&CK to document common tactics, techniques, and procedures that Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) use against Windows networks. It began as a documentation research project called "FMX," which investigated endpoint telemetry data and analytics usage with the aim of improving post-compromise detection. ATT&CK became the basis for testing the efficacy of sensors and analytics and is now the common language of cybersecurity offense and defense teams.[4]
By spring 2021, the initially released ATT&CK framework had undergone many changes and was in its ninth version.
Overview

The framework covers four conceptual issues with the overarching aim to assist proactive offense rather than reactive defense.[5]
- Behaviors: ATT&CK reflects patterns of use rather than indicators of activities, such as domains, IP addresses, file hashes, registry keys, because threat actors can easily change the latter. They are useful for detection, but they don't holistically capture how threat actors interact with systems.
- Models: ATT&CK is meant to provide less high-level lifecycle and Cyber Kill Chain models because too much abstraction makes them unhelpful.
- Observation: ATT&CK relies on observed incidents so that the framework can be applied to real environments.
- Taxonomy: ATT&CK emphasizes generating and using common terminology across incidents for the sake of comparison, such as TTPs.
Terminology
Tactics
Tactics refer to the purpose behind an adversarial technique. It is the goal for performing the action, such as stealing credentials or gaining remote access.
Techniques
Techniques encompass the conceptual method for achieving the tactical goal in question.
Procedures
Procedures refer to the actual implementation of the techniques.
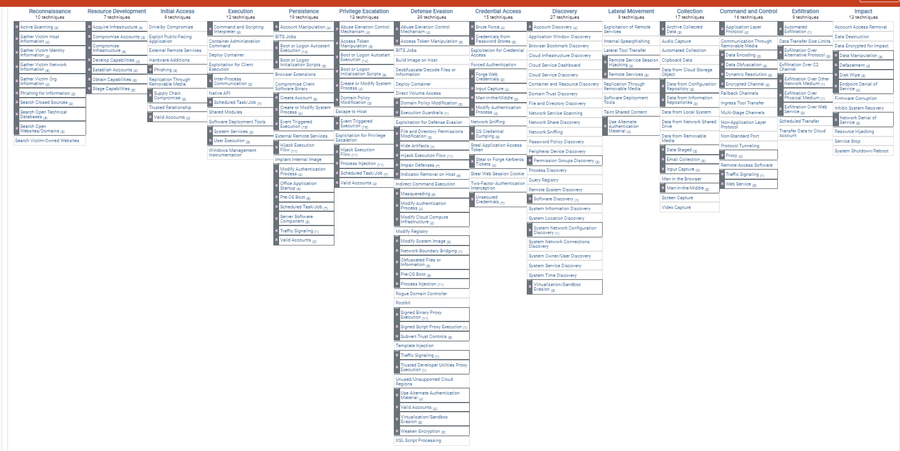
Enterprise
ICS
ATT&CK for Industrial Control Systems (ICS) focuses on adversaries with the goal of disrupting an industrial control process, destroying property or causing temporary or permanent harm or death to humans[6] by attacking ICS generally found in sectors such as electric, water/wastewater, oil/natural gas, transportation, chemical, pharmaceutical, pulp and paper, food and beverage, and manufacturing.[7]
ATT&CK Evaluations
MITRE Engenutiy (ME) provides vendors with assessments of their ability to defend against TTPs by emulating known behaviors and exercising common ATT&CK techniques, as well as push the market to more effectively secure the world’s networks. ME publishes the results to inform the community. The evaluations do not reflect competitive analysis; there are no scores, rankings, or ratings. However, they do compare how vendors approach threat detection.[8]
