Address Supporting Organization: Difference between revisions
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
===Global Policies=== | ===Global Policies=== | ||
The ASO does not directly develop policy on Internet number resources but instead ensures that each RIR follows its Policy Development Processes. Global policies are made when there is agreement among all of the RIRs according to their policy development processes and ICANN | The ASO does not directly develop policy on Internet number resources but instead ensures that each RIR follows its Policy Development Processes. Global policies are made when there is agreement among all of the RIRs according to their policy development processes and ICANN and require specific actions on the part of [[PTI]] to be implemented.<ref>[https://aso.icann.org/about-the-aso/ About the ASO]</ref> The global numbers community uses the Global Policy Development Process (GPDP) to guide the [[PTI]] on what actions to take. | ||
====GPDP==== | |||
# A proposed global policy can be submitted either to one of the RIR policy fora (via mail lists or public policy meeting) or to the ASO Address Council directly. | |||
# The members of the Address Council will request that the global policy proposal be placed on the agenda for next open policy meeting in each region, in accordance with the applicable policy process. | |||
# After consideration of the proposal at each of the RIR meetings, the staff of the RIRs will work with each other, and with the policy proposer to document the common elements of such outcomes. | |||
#This common text will be ratified by each RIR, by methods of its own choosing. | |||
#This ratified common text is the proposed global policy proposal that is forwarded to the ASO Address Council, which will either | |||
#:a. pass it to ICANN for ratification as a global policy, or | |||
#:b. advise the NRO Executive Council that the Address Council has concerns as an outcome of its review and that the proposal requires further review within the public policy development process, or | |||
#:c. request the NRO Executive Council for an extension of time to complete the review of the proposal. | |||
#If the AC has passed the proposal onto ICANN Board, the directors will review it and consult with the AC or RIR through the NRO as well as other ICANN bodies, if necessary. | |||
# After 60 days, the ICANN Board will then | |||
#:a. accept the proposal by a simple majority vote; or | |||
#:b. reject the proposed policy by a supermajority (2/3) vote; or | |||
#:c. by a simple majority vote request changes to the proposed policy; or | |||
#:d. take no action, ''in which case the proposal becomes global policy''. | |||
#If the ICANN Board rejects the proposal, it must provide the ASO a document of its reasoning and concerns within 60 days. | |||
#After deliberation among the RIRs, the NRO Executive Council can indicate to the ASO that it may submit a modified or the same exact proposal to the ICANN Board. | |||
#The resubmitted proposal becomes global policy unless the ICANN Board rejects it by a supermajority (2/3) vote; if it is rejected, the RIRs and ICANN enter into mediation.<ref>[https://aso.icann.org/policy/global/global-policy-development-process/ ASO GPDP]</ref> | |||
===Regional Policies=== | ===Regional Policies=== | ||
Revision as of 14:23, 5 January 2021
 | |
| Type: | Supporting Organization |
| Industry: | IP Addresses |
| Founded: | 1999 |
| Website: | ASO.ICANN.org |
The Address Supporting Organization (ASO) is mandated with reviewing and developing recommendations for policies on Internet Protocol addresses and advising the ICANN Board on issues related to their operation, assignment, and management.[1]
Overview[edit | edit source]
Established in 1999, the Address Supporting Organization is composed of an Address Council (AC), with representatives from each of the five autonomous RIRs:[2]
Three representatives are appointed from each RIR, which have their own independent election processes.[3] The Council then elects a chair who appoints the vice-chairs.
Policymaking in ICANN[edit | edit source]
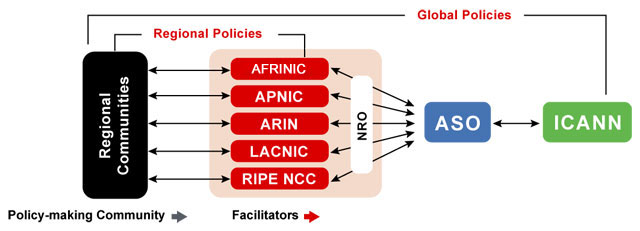
Global policies govern how Public Technical Identifiers (PTI) issue Internet number resources to the RIRs, which then distribute them among their members based on regional policies.
Global Policies[edit | edit source]
The ASO does not directly develop policy on Internet number resources but instead ensures that each RIR follows its Policy Development Processes. Global policies are made when there is agreement among all of the RIRs according to their policy development processes and ICANN and require specific actions on the part of PTI to be implemented.[4] The global numbers community uses the Global Policy Development Process (GPDP) to guide the PTI on what actions to take.
GPDP[edit | edit source]
- A proposed global policy can be submitted either to one of the RIR policy fora (via mail lists or public policy meeting) or to the ASO Address Council directly.
- The members of the Address Council will request that the global policy proposal be placed on the agenda for next open policy meeting in each region, in accordance with the applicable policy process.
- After consideration of the proposal at each of the RIR meetings, the staff of the RIRs will work with each other, and with the policy proposer to document the common elements of such outcomes.
- This common text will be ratified by each RIR, by methods of its own choosing.
- This ratified common text is the proposed global policy proposal that is forwarded to the ASO Address Council, which will either
- a. pass it to ICANN for ratification as a global policy, or
- b. advise the NRO Executive Council that the Address Council has concerns as an outcome of its review and that the proposal requires further review within the public policy development process, or
- c. request the NRO Executive Council for an extension of time to complete the review of the proposal.
- If the AC has passed the proposal onto ICANN Board, the directors will review it and consult with the AC or RIR through the NRO as well as other ICANN bodies, if necessary.
- After 60 days, the ICANN Board will then
- a. accept the proposal by a simple majority vote; or
- b. reject the proposed policy by a supermajority (2/3) vote; or
- c. by a simple majority vote request changes to the proposed policy; or
- d. take no action, in which case the proposal becomes global policy.
- If the ICANN Board rejects the proposal, it must provide the ASO a document of its reasoning and concerns within 60 days.
- After deliberation among the RIRs, the NRO Executive Council can indicate to the ASO that it may submit a modified or the same exact proposal to the ICANN Board.
- The resubmitted proposal becomes global policy unless the ICANN Board rejects it by a supermajority (2/3) vote; if it is rejected, the RIRs and ICANN enter into mediation.[5]
Regional Policies[edit | edit source]
Each RIR distributes Internet number resources to its members according to policies that have been defined by its regional community. Each RIR community proposes, discusses, accepts, or rejects policies using a consensus-based policy development process. Anyone can submit a policy proposal for consideration as RIR membership is not required.[6]
ASO History[edit | edit source]
In July 1999, when the three Regional Internet Registries which existed then, APNIC, ARIN, and RIPE NCC submitted their proposal for the creation of the ASO on the basis of the Memorandum of Understanding; which allows for the creation of a body such as the ASO as an extension of the NRO.
ICANN approved the proposal at its meeting in Chile, and the ASO was subsequently created in October 1999, when the representatives of APNIC, ARIN, RIPE NCC, and ICANN signed the MoU. LACNIC was later recognized as the 4th RIR and it signed the agreement on October 30th, 2002. The Memorandum of Understanding was modified in October 2004, and signed by ICANN and the NRO, which signed on behalf of all the RIRs. When ICANN decided to recognize AfriNIC as the fifth global RIR the representatives of AfriNIC signed the MoU, and it was incorporated as the 5th NRO member.[7]
ASO Address Council[edit | edit source]
The main responsibilities of the ASO Address Council are:
- Fulfilling its role in the global policy development process based on the requirements included in this process;
- Maintaining communication with ICANN and providing recommendations related to various policies and RIR recognition;
- Ensuring full support, guidance, and advice for ICANN's Board related to the allocation policy for number resource;
- The development of procedures for business management and support their responsibilities especially in the case of Address Council Chair. [8]
Address Council Members[edit | edit source]
The council consists of 15 members, with three members from each of the five RIRs, with two being selected by each RIR's regional policy forum and one selected by each RIR Executive Board.[9]
| Council Member | Region | Term |
|---|---|---|
| Wafa Dahmani Zaafouri* | AFRINIC | Jan 2020 - 31 Dec 2020 |
| Mike Silber | AFRINIC | Jan 2020 - 31 Dec 2022 |
| Mukhangu Noah Maina | AFRINIC | Jan 2018 - 31 Dec 2020 |
| Brajesh Jain | APNIC | Jan 2019 - 31 Dec 2020 |
| Simon Sohel Baroi* | APNIC | Jan 2020 - 31 Dec 2020 |
| Aftab Siddiqui* Chair | APNIC | Jan 2020 - 31 Dec 2020 |
| Louis Lee | ARIN | Jan 2019 - 31 Dec 2021 |
| Kevin Blumberg* Vice-Chair | ARIN | Jan 2018 - 31 Dec 2020 |
| Martin Hannigan | ARIN | Jan 2020 -31 Dec 2022 |
| Ricardo Patara | LACNIC | Jan 2019 - 31 Dec 2021 |
| Jorge Villa Vice-Chair | LACNIC | Jan 2018 - 31 Dec 2020 |
| Esteban Lescano* | LACNIC | April 2020 - 31 March 2021 |
| Filiz Yilmaz | RIPE NCC | Jan 2020 - 31 Dec 2022 |
| Nurani Nimpuno | RIPE NCC | Jan 2019 - Dec 2021 |
| Herve Clement* | RIPE NCC | Jan 2018 - 31 Dec 2020 |
*Board-appointed member to the ASO AC
ICANN Board members[edit | edit source]
Consistent with the ASO Memorandum of Understanding and ICANN Bylaws, the Address Supporting Organization Address Council (ASO AC) is responsible for appointing Seats, nine and ten to the ICANN Board of Directors. For more information about the selection processes for current and previous appointments please follow the link.[10]
