Generic Names Supporting Organization: Difference between revisions
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
''Contracted Parties'' | ''Contracted Parties'' | ||
* [[ | * [[Registrars Stakeholder Group]], 3 appointments | ||
* [[Registries Stakeholder Group|Registry Stakeholder Group]], 3 appointments | * [[Registries Stakeholder Group|Registry Stakeholder Group]], 3 appointments | ||
[[File:GNSO Council.jpg|thumb|GNSO Council, as photographed at ICANN 60 in Abu Dhabi in November 2017.]] | [[File:GNSO Council.jpg|thumb|GNSO Council, as photographed at ICANN 60 in Abu Dhabi in November 2017.]] | ||
Revision as of 21:32, 16 December 2020
The Generic Names Supporting Organization (GNSO) is a policy-development body which is responsible for developing and recommending to the ICANN Board substantive policies relating to generic top-level domains (gTLDs). The GNSO is formed of Stakeholder Groups, themselves composed of Constituencies, which together form one Supporting Organization to form consensus, set policy, and make evidence-informed recommendations.[1] The GNSO was previously known as the Domain Name Supporting Organization (DNSO), which it replaced in 2003.
Policy development within the GNSO is governed by the GNSO Council. The Council meets 12 times per year; four times face-to-face (three times at ICANN public meetings, and once at the Council Strategic Planning Session), and eight times via webinar.
Overview[edit | edit source]
The main objective of the GNSO is to ensure that gTLDs operate in a fair and orderly manner across the global Internet, without hindering innovation or competition. As ICANN sets policy by contract, the GNSO develops policy with the involvement of both the contracted and non-contracted parties who hold equal influence and equal voting rights. In addition, two independent appointments to the Council of non-voting members are made by ICANN's Nominating Committee.
Non-Contracted Parties
- Non-Commercial Users Stakeholder Group, 6 appointments
- Commercial Stakeholder Group, 6 total appointments coming from the 3 constituencies
- Commercial and Business Users Constituency, 2 appointments
- Intellectual Property Interests Constituency, 2 appointments
- Internet Service and Connection Providers Constituency, 2 appointments
Contracted Parties
- Registrars Stakeholder Group, 3 appointments
- Registry Stakeholder Group, 3 appointments

GNSO Council[edit | edit source]
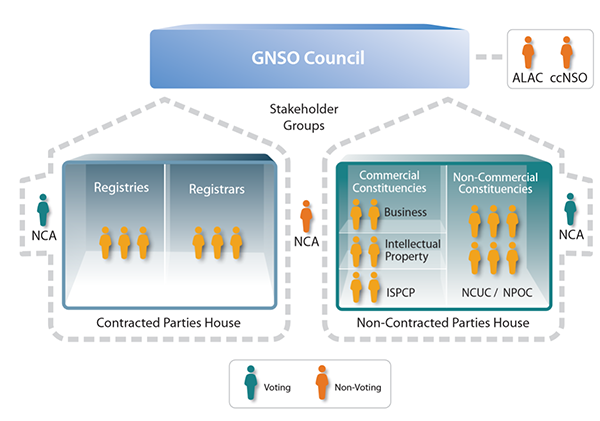
The GNSO Council consists of 21 members, 20 of whom are voting members, and the Council has two houses. Stakeholder Groups appoint 18 of its members to be involved in ICANN's multistakeholder model. Philippe Fouquart is the current Chair and will serve until October 2021. Pam Little, Registrar Stakeholder Group Council representative, was re-elected as the Contracted Party House GNSO Council Vice-Chair. Tatiana Tropina, Non-Commercial Stakeholder Group representative, was elected as the Non-Contracted Party House GNSO Council Vice-Chair.
Members Include:
NCAs[edit | edit source]
- Tom Dale, Contracted Party House, Asia Pacific (AGM 2021)
- Olga Cavalli, non-voting member, Latin America Caribbean (AGM 2022)
- Carlton Samuels Non-Contracted Party Hous, Latin America Caribbean (AGM 2021)
GNSO Council Liaisons & Observers[edit | edit source]
- Maarten Simon, ccNSO liaison, Europe
- Jeffrey Neuman, GNSO Liaison to the GAC, North America
- Cheryl Langdon-Orr, ALAC Liaison, Asia Pacific
Contracted Party House[edit | edit source]
- Pam Little, Vice-Chair, Asia Pacific, term ends AGM 2021
Registries Stakeholder Group[edit | edit source]
- Kurt Pritz, North America, term expires AGM 2022
- Sebastien Ducos, Asia Pacific, term expires AGM 2021
- Maxim Alzoba, Europe, term expires AGM 2022
Registrars Stakeholder Group[edit | edit source]
- Pam Little, Asia Pacific, term ends AGM 2021
- Greg DiBiase, North America, term ends AGM 2021
- Kristian Ørmen, Europe, term ends AGM 2022
Non-Contracted Party House[edit | edit source]
- Philippe Fouquart, Chair, Europe, term ends AGM 2022
- Tatiana Tropina, Vice-Chair, Europe, term ends AGM 2021
Commercial Stakeholder Group[edit | edit source]
Commercial and Business Users - Business Constituency
- Marie Pattullo, Europe, term ends AGM 2021
- Mark Datysgeld, Latin America Caribbean, term ends AGM 2021
Intellectual Property Interests - Intellectual Property Constituency
- John McElwaine, North America, term ends AGM 2021
- Flip Petillion, Europe, term ends AGM 2022
ISP Interests - ISP Constituency
- Philippe Fouquart, Europe, term ends AGM 2020
- Osvaldo Novoa, Latin America Caribbean, term ends AGM 2021
Non-Commercial Stakeholder Group[edit | edit source]
- Wisdom Donkor, Africa, term ends AGM 2022
- Stephanie Perrin, North America, term ends AGM 2022
- Tatiana Tropina, Europe, term ends AGM 2021
- Juan Manuel Rojas, Latin America Caribbean, term ends AGM 2022
- Farell Folly, Africa, term ends AGM 2021
- Tomslin Samme-Nlar, Asia Pacific, term ends AGM 2022
GNSO Development Process[edit | edit source]
The GNSO is the primary engine within the ICANN community for developing, recommending changes, and making modifications to generic top-level domain policies. The GNSO aims to identify ways to improve the inclusiveness and representativeness of its work while increasing its effectiveness and efficiency.
An important GNSO improvement was the development of recommendations for the new GNSO policy development process. The ICANN Board launched a set of recommendations for improving the effectiveness of the GNSO in June 2008. These recommendations were related to GNSO activities, operations, and structure.
GNSO Improvements[edit | edit source]
GNSO Standing Committee on Improvements Implementation (SCI). The SCI will be responsible for reviewing and assessing the effective functioning of recommendations provided by the Operational Steering Committee (OSC) and Policy Process Steering Committee (PPSC) and approved by the GNSO Council. The main areas of GNSO improvements which were approved by the Board, and are being implemented by the GNSO, are classified into five main categories:
- The creation of a Working Group Model
- Revising the PDP (Policy Development process)
- The restructuring of GNSO Council
- Communication improvement and better coordination between ICANN structures
- Improving constituency procedures [2]
GNSO Policy Development process[edit | edit source]
The Policy Development Process (PDP) Updates are one-page documents prepared by ICANN staff to inform the Governmental Advisory Committee (GAC) and other interested parties about potential opportunities to engage in and contribute to on-going GNSO PDP efforts. They are published on a regular basis and translations of these can be found on the GAC website. Please, also refer to our GNSO Policy Briefing for information on these and other GNSO activities.
Implementation of URS[edit | edit source]
In September 2012, ICANN senior executive Kurt Pritz sent a public email to GNSO Council Chairman Stephane Van Gelder advising him that URS implementation could begin after a year of delay. Implementing URS included a pair of open meetings in Fall 2012, including one at ICANN 45 in Toronto. ICANN acknowledged the role played by the GNSO Council in developing and approving the model and said they were willing to "work in whichever way the GNSO wishes to proceed".[3]
ICANN Supporting Organizations and Advisory Committees[edit | edit source]
Apart from the GNSO, there are other Supporting Organizations and Advisory Committees which help ICANN to fulfill its objectives. They include:
- Address Supporting Organization (ASO)
- Country Code Domain Name Supporting Organization (ccNSO)
- At-Large Advisory Committee (ALAC)
- Governmental Advisory Committee (GAC)[4]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ GNSO.ICANN.org
- ↑ GNSO improvements
- ↑ URS Implementation Finally to Commence Under GNSO Direction. Internet Commerce Association. Published 2012 September 20.
- ↑ ICANN supporting organizations
