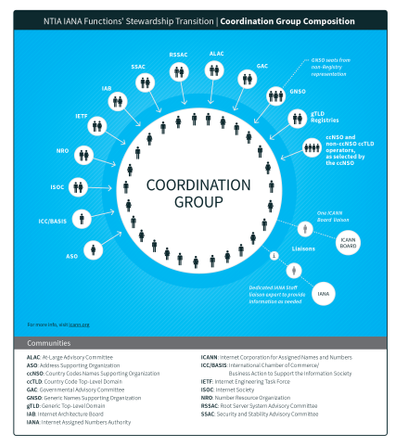
IANA Stewardship Transition Coordination Group
The IANA Stewardship Transition Coordination Group (ICG) was formed by ICANN in response to the NTIA's announcement on 14 March 2014 that it intended to transition stewardship of the IANA functions to the global multistakeholder community. In the announcement, the NTIA asked ICANN to convene a multistakeholder process to develop a proposal for the transition. After gathering community views and input, the ICG was formed, consisting of 30 members from 13 different communities. The ICG was given the task of coordinating "the development of a proposal among the communities affected by the IANA functions."[1]
The IANA functions consist of three separate categories: domain names, number resources, and protocol parameters. The ICG tasked the operational communities for each of the IANA functions to develop a proposal for their part of the IANA functions. Once all of the required proposals are received it is the job of the ICG to combine them into one complete and final proposal.[2]
Working Groups[edit | edit source]
The ICG determined that the proposals concerning the different functions should be developed by the directly affected communities. Each of these three communities created working groups to develop their respective proposals.
In addition to the three proposal development processes directly relating to the IANA functions, the ICG initiated a process for Enhancing ICANN Accountability, due to concerns expressed by the community about post-transition accountabilty.
Domain Names System functions and the CWG-Stewardship[edit | edit source]
The communities directly affected by the DNS Functions can be divided into two subcategories: gTLDs and ccTLDs. With respect to these functions, the CWG-Stewardship was formed with the GNSO, ccNSO, ALAC, GAC, and SSAC as the chartering organizations.[3]
Numbering Resources and the CRISP TEAM[edit | edit source]
The operational community for the number resource segment of the IANA functions include the NRO, ASO, and the five RIRs. Together these organizations formed the Consolidated RIR's IANA Stewardship Proposal Team (CRISP Team).[4]
Protocol Parameters and the IANAPLAN WG[edit | edit source]
The operational community for the protocol parameters functions include the IETF and IAB. Together they formed the IANAPLAN Working Group.[5]
Enhancing ICANN Accountability and the CCWG-Accountability[edit | edit source]
During initial discussions on the IANA Transition, the community raised concerns about the impact of the transition on ICANN Accountability. These concerns led to the formation of the CCWG-Accontability. Within the working group, two work streams were developed. Work Stream 1 is concerned with accountability mechanisms that are necessary to be have in place prior to the transition. Work Stream 2 focused on processes that may extend beyond the transition if necessary.
The chartering organizations include: GNSO, ccNSO, ALAC, GAC, ASO and SSAC.
Composition of ICG[edit | edit source]